
Critics of the blockchain have highlighted several issues preventing it from becoming a mainstream financial solution. As the cryptocurrency world has expanded over the past decade, several new projects have attempted to solve blockchain tech’s biggest problems. Algorand is a new kid on the block making waves in the crypto world. This article explores Algorand and how the blockchain plans to revolutionise the industry.
What is Algorand?
Algorand is a public blockchain protocol that utilises smart contracts to deploy decentralized applications on its network. Algorand builds upon existing blockchain technology in an attempt to solve the blockchain trilemma. The trilemma is a theory that any given blockchain must sacrifice either decentralization, scalability or security to reap the benefits of the other two.
The developers aim to conquer this by maintaining the security of other blockchains while implementing lightning-fast transaction speeds. The enhanced confirmation times help improve the scalability of the Algorand blockchain, making it perfect for hosting tailored dApps or building blockchains. ALGO is the native cryptocurrency used within the Algorand ecosystem.
The Algorand network was founded in 2017 by Silvio Micali, a Massachusetts Institute of Technology professor and Turing award winner. He spent two years developing the blockchain before releasing it to the community in June 2019.
Did You Know?
Algorand underwent a capital raise before its release in 2019. This venture was a resounding success, with various investors demonstrating interest in the product. By 2018, the Algorand team had secured $62 million USD in funding.
How does Algorand work?
The Algorand platform uses a combination of new technology and concepts from the cryptocurrency world.
Pure Proof of Stake (PPoS)
The Algorand consensus protocol employs a custom version of the Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism to validate transactions on the protocol. Traditional PoS mechanics have high requirements for users to operate nodes. For example, Ethereum stakers must lock up 32 ETH – equivalent to over $50,000 USD – to run a node. On the other hand, Algorand only requires validators to stake a single ALGO token.
The Pure Proof of Stake model helps address two key issues in the blockchain trilemma. Decentralization is encouraged as anybody can run their own node and validate transactions, instead of only those that can afford a large upfront investment. Furthermore, Algorand’s consensus protocol allows transactions on the blockchain to be finalised quickly, improving scalability.
The Algorand Foundation
The Algorand Foundation is a non-profit foundation that oversees the development, functioning and economic security of the Algorand blockchain. The Foundation is responsible for decentralizing the network’s governance, forming business partnerships and keeping the Algorand community informed.
The Algorand Foundation offers various programs to incentivise creativity and development within the blockchain’s ecosystem. They reward community members for outstanding participation, run university lectures and help fund new dApps deployed on Algorand’s blockchain.
Nodes
Nodes are vital to how blockchains work. Each node forms a part of the distributed ledger that comprises a decentralized network. A node is a computer server that constantly runs blockchain software to validate transactions and new information on the chain. The more nodes a blockchain has running around the world, the harder it is to attack.
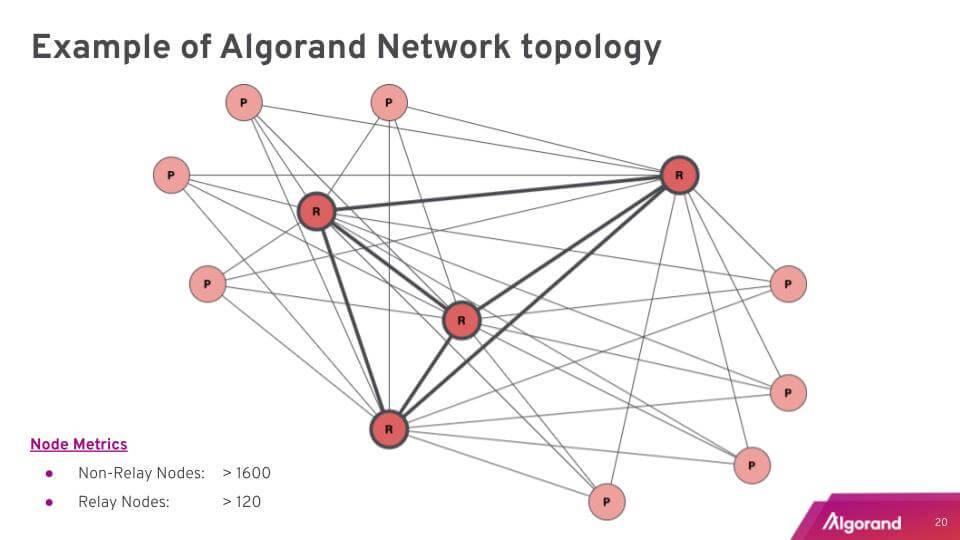
Figure 1 – Algorand network architecture
Participation nodes
Participation nodes are in charge of voting on new blocks and validating transactions. These nodes support the PPoS consensus mechanism and operate similarly to staking nodes on other protocols. Participation node operators can lock up ALGO tokens to give themselves a chance to validate a transaction (block) and receive a reward. Users must lock up at least 1 ALGO to run a participation node.
Participation nodes are connected to relay nodes, but typically not to other participation nodes.
Tip
Algorand’s Pure Proof of Stake consensus mechanism randomly selects participation nodes to confirm transactions. Although users can run a node with a single ALGO, the “random” algorithm weights potential validators by the amount of ALGO staked. So, the more ALGO locked up, the higher the chance of a node receiving block rewards.
Relay nodes
Relay nodes are one of the key elements of Algorand’s efficient and fast blockchain. These nodes serve as communication hubs on the network and can coordinate simultaneous validations.
Relay nodes perform checks for duplicates and signatures on validated blocks. The relay node will spread this information to its connected nodes if the new block passes the review. This removes multiple steps from older validation processes.
Think of relay nodes like a team manager. They are responsible for ensuring their “teams” (groups of connected nodes) are up-to-date, and communication across “employees” (participation nodes) remains open. The relay node will also double-check all the work its employees submit. If a worker’s done a poor job, the relay node will inform their team it needs to be fixed.
Two-tiered chain structure
Legacy blockchains like Bitcoin and the original Ethereum were single-layered blockchains. However, this structure tends to present issues with scalability and transaction speed. Newer networks like Algorand have developed multi-layered blockchains to improve efficiency and support the deployment of decentralized applications (dApps).
Algorand’s first layer is intended for simple transactions, minting new tokens and easily executed smart contracts. In that sense, tier 1 of Algorand’s blockchain has similar functionality to Bitcoin’s. The second layer is intended for dApps and more complicated smart contracts. This multi-tiered system prevents Algorand’s network speeds from being throttled by basic transactions while running convoluted applications.
The two layers work like two separate departments in a business. Layer one is like accounting, while layer two operates as a software development team. The two branches are in communication, when necessary, but for the most part, work independently.
What makes Algorand unique?
The Algorand network’s Pure Proof of Stake consensus mechanism has several unique attributes. For example, those that misbehave on other PoS protocols are punished via “slashing”, where the bad actors’ staked tokens are re-claimed (or burned) by the network. However, Algorand’s blockchain has no slashing mechanism. Instead, the blockchain simply ignores the malicious person and enters recovery mode.
Did You Know?
Algorand’s lack of slashing is a controversial decision. The reason it ignores bad actors is to ensure the blockchain maintains 100% efficiency. The process of slashing could substantially slow transaction speeds and congest dApp functionality. However, the lack of punishment may also encourage malicious stakers to attack the network repeatedly.
The Algorand protocol is also a first-of-its-kind technology when it comes to forking. On most other blockchains, if two blocks are solved within milliseconds of each other, the network branches off into two different chains. This is known as an accidental fork. These forks can cause transactions to appear finalised, but remain unfulfilled until the fork is closed.
Algorand’s technology is designed so its chain never forks. Once a block has been added and a transaction finalised, it is permanent. Two different blocks can not be added to a chain in the same chronological position. Therefore, users can send and receive without worrying about how long the transaction takes to finalise.
Algorand’s use cases
Decentralized applications and NFTs
Algorand’s support for smart contracts alongside its multi-tiered chain structure make it a natural choice for hosting dApps and NFTs. The blockchain already supports well-known dApps like Algofi (lending service), Yieldly (decentralized exchange) and ANote Music (music royalty exchange).
Servicing businesses
Silvio Micali designed Algorand as a blockchain that could service businesses. The network’s fast transaction finality and low gas fees have led to Algorand being a desirable blockchain for payment services. For example, the sustainability business Global Carbon Holding has partnered with Algorand to tokenise credit for offsetting carbon production.
Stablecoins
In the latter stages of 2020, Algorand implemented the popular stablecoin USD Coin (USDC) into its network.
What is ALGO?
ALGO is Algorand’s native cryptocurrency. ALGO tokens have two primary use cases. Firstly, they are used as a reward for participation in the blockchain – including both stakers and token holders. Additionally, ALGO is the native medium of exchange for most applications on the Algorand network. It is also used to pay transaction fees.
ALGO has a maximum total supply of 10 billion ALGO, the entirety of which will be in circulation by 2030.
Interesting Fact
Algorand is one of the only cryptocurrencies to reward holders automatically. Owners of more than 1 ALGO in a supported wallet (such the official Algorand Wallet or a Ledger wallet) receive additional ALGO tokens added directly to their balance at an APY of approximately 6-8%. ALGO held on most exchanges will not passively earn interest.
How to buy ALGO
Investors can buy ALGO from the most prominent cryptocurrency exchanges. Swyftx is a popular exchange in Australia and New Zealand that supports buying ALGO with low fees. ALGO purchased on Swyftx can be stored in a personal multi-token wallet.
Summary
Algorand is an exciting new network attempting to address the decade-old blockchain trilemma. Algorand’s primary selling point is its efficiency, boasting impressive transaction speeds and low fees. The inherent scalability of its blockchain gives Algorand the potential to be one of the most popular networks for dApp developers. However, the full scope of Algorand’s technology is yet to be realised.
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.
