If you’ve delved into the complex world of mining cryptocurrency, you may have come across the terms Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
Each are consensus mechanisms used to confirm transactions that take place on a blockchain and negate the need for a trusted third party. While they have many overlapping qualities, there are key differences between the two that relate to the how and the who of creating new blocks on a blockchain system. This article will delve into Proof of Work and Proof of Stake consensus algorithms in-depth as well as listing the pros and cons of both.
What’s a consensus mechanism?
Before explaining what each of the protocols are, it’s important to grasp an understanding of consensus algorithms.
For cryptocurrency to remain secure, and transactions to remain authentic, a network of computers known as nodes exists to verify and regulate all transactions on a blockchain network. This procedure is known as a consensus algorithm or ‘mechanism’, and it ensures that all peers on a blockchain reach an agreement around the validity of new blocks on the network among distributed nodes.
Proof of Stake and Proof of Work are two of the most widely used consensus algorithms.
What is Proof of Work?
When the creator of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto, was developing the first-ever cryptocurrency, the challenge was to find a way to verify transactions without the need for a trusted third party. They achieved this by using a Proof of Work consensus algorithm.
A blockchain ledger contains a record of transactions that are organised in a chain of blocks. A Proof of Work system is used to determine the validity of new transactions and helps reach a consensus on the blockchain. This is extremely important in preventing tampering with transactions. If a faulty transaction is broadcast to the network of nodes on a blockchain network, it will quickly be rejected. This allows Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency transactions to be processed in a secure manner without the need for a trusted third party.
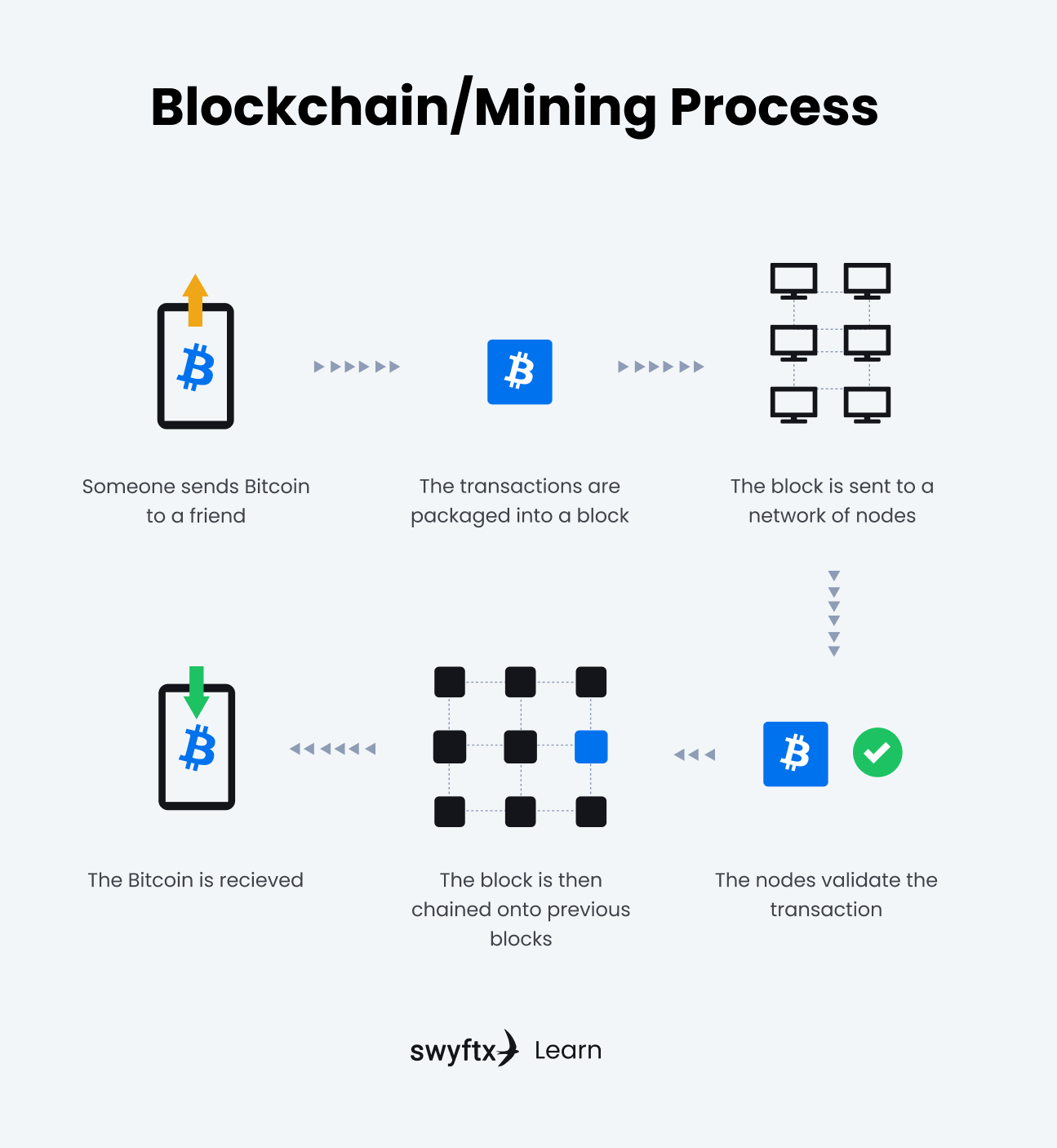
Figure 1 – The blockchain/mining process explained
A Proof of Work blockchain uses mining for verifying transactions and creating new tokens. This process requires large amounts of computing power which means energy consumption and electricity costs are often extreme.
Did You Know?
The Proof of Work (PoW) consensus algorithm was in fact not originally conceived for cryptocurrency. The concept was originally introduced in the 1990s as a means to help reduce and prevent email spam.
Examples of Proof of Work blockchains
As mentioned above, Proof of Work was first introduced into cryptocurrency and popularised by Bitcoin in 2009. Many other coins like Litecoin (LTC) and Dogecoin (DOGE) would later adopt this type of consensus algorithm. Litecoin was one of the first ever altcoins that was created to offer improvement on the speed, cost and efficiency of Bitcoin transactions. Its code was based off Bitcoin’s and was later forked to create Dogecoin. Dogecoin is a meme coin that was created in 2013 as a joke cryptocurrency to poke fun at Bitcoin.
What is Proof of Stake?
Proof of Stake has many similar mechanics to Proof of Work, with a few key differences. It was first conceptualised in 2012 by two developers called Scott Nadal and Sunny King to solve the perceived energy consumption issues of the PoW system.
The Proof of Stake model uses an alternative method to verify transactions and reach consensus. While Proof of Work mechanisms reward miners for solving complex mathematical equations in order to verify transactions and create new blocks, Proof of Stake systems selects a user to create the new blocks instead. To be selected, this user must stake a certain amount of cryptocurrency.
Staking is the process of locking up a balance of tokens as a security deposit in order to earn the right to verify transaction on a Proof of Stake blockchain. If the transaction is verified correctly, the user who staked their tokens will receive staking rewards.
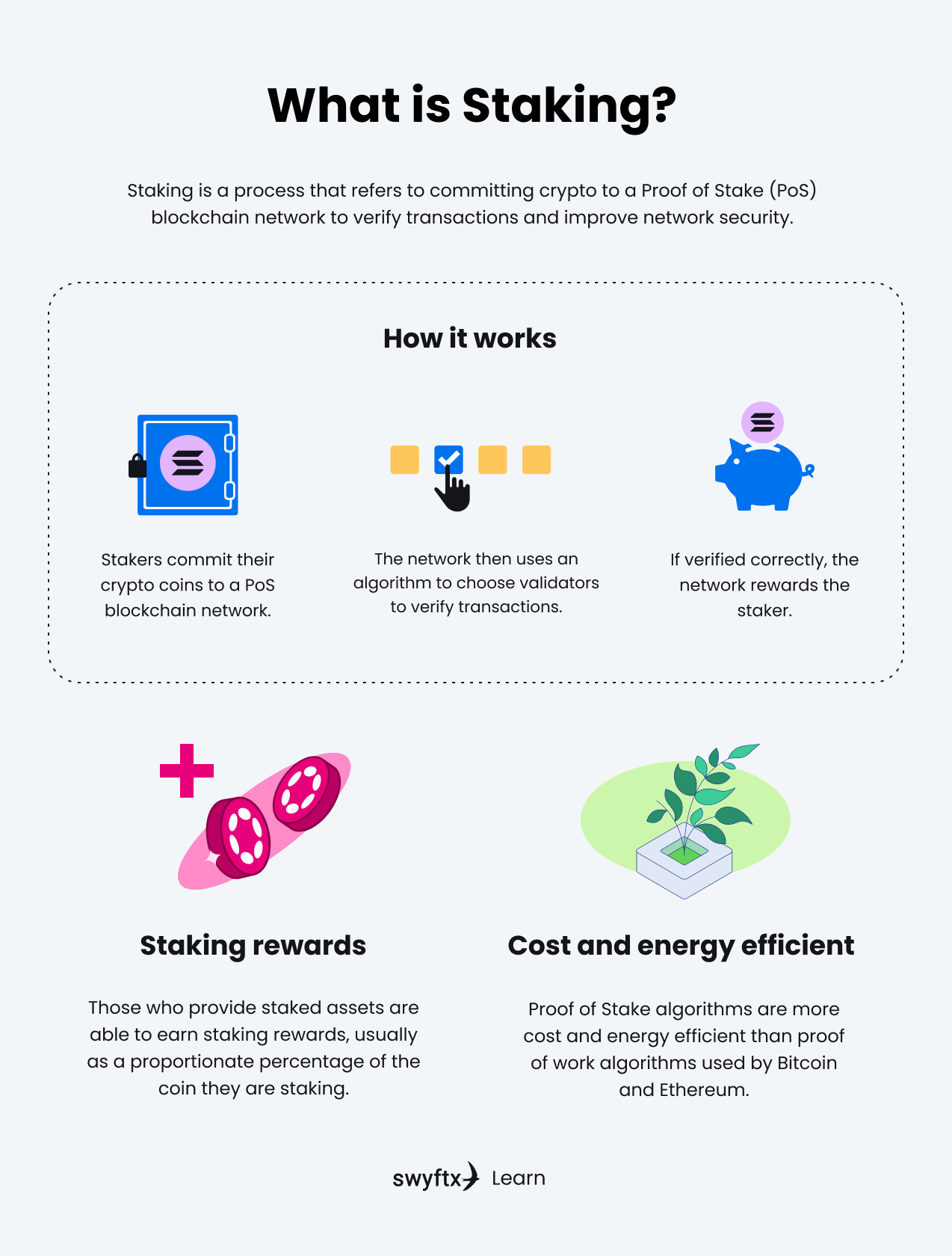
Figure 2 – Staking explained
Examples of Proof of Stake blockchains
The last few years has seen the emergence of large Proof of Stake blockchains like Cardano, Polkadot and Avalanche. Ethereum, which was originally designed as a PoW blockchain is in the process of transitioning to a PoS blockchain which is being referred to as Ethereum 2.0. This overhaul of the blockchain seeks to resolve some of the core issues of the Ethereum network (I.e. slow and expensive transactions) to make Ethereum more scalable and secure.
Key Takeaway
Stake selects users to verify transactions and create new blocks based on how much cryptocurrency they have staked. This type of consensus algorithm is said to use about 99.95% less energy that Proof of Work.
Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
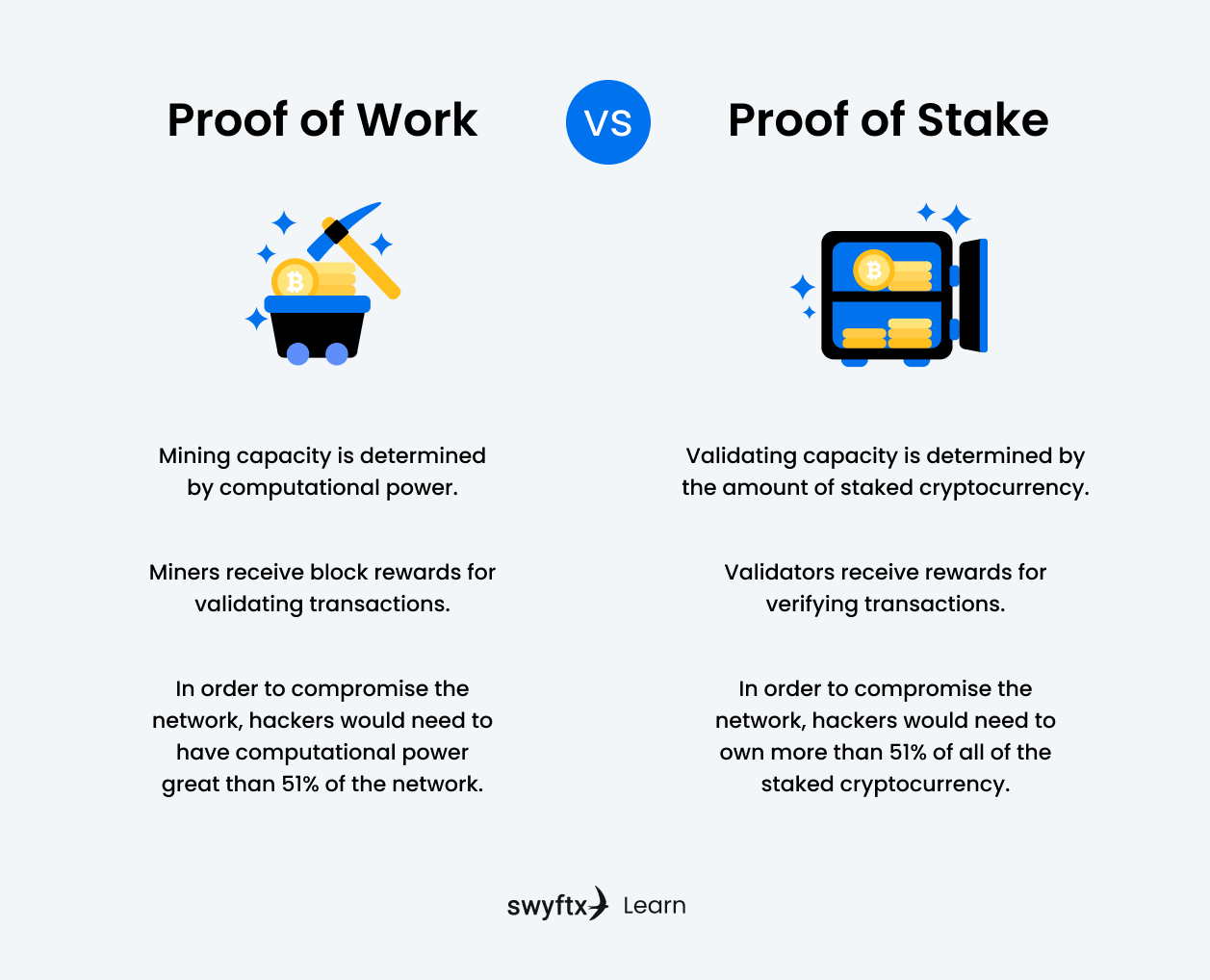
Figure 2 – Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
Pros and cons
Proof of Work
Pros
- Difficult and costly to attack
- Highly decentralized
- Miners receive rewards for creating new blocks
Cons
- Mining requires large amounts of computational power and electricity
- Generally slow and expensive transactions
- Some PoW networks are susceptible to 51% attacks
Proof of Stake
Pros
- Fast transactions and high level of scalability
- Very energy efficient, approximately 99% more so than PoW
- Stakers receive rewards for validating transactions
Cons
- PoS has yet to prove itself at scale compared to PoW
- More centralized than PoW, as it favours users with high amounts of tokens
- Some networks require users to lock up their staking assets
Summary
There is no correct answer as to which consensus algorithm is superior as they both have their pros and cons. Proof of Work was the original consensus algorithm that strongly focuses on decentralization. Proof of Stake was conceived to solve the lingering issues associated with Proof of Work such as transaction speeds and costs, however, many believe it too heavily favours entities with large token holdings. At this stage, it appears that Proof of Stake algorithms are growing at an accelerated rate compared to Proof of Work so the next few years will be telling as to which comes out on top.
Next lesson
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.

 Article read
Article read