
Ethereum is a rapidly growing blockchain notorious for its high gas fees. In some instances, the gas fees are higher than the amount of Ethereum in the transaction. These high gas fees are due to limitations of the Ethereum blockchain, thus creating a need for robust scaling solutions. Polygon is a leading scaling solution for the Ethereum blockchain. This article explains what Polygon is and uncovers all the components that build up the network, including the MATIC token.
What is Polygon?
In 2017, the Matic Network was founded by Jayant Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, and Anurag Arjun. Later, Matic was rebranded to Polygon, however, the MATIC token kept its original name.
The Polygon project is a protocol and a framework for developing and establishing connections with Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks. Polygon’s interoperable network aims to solve the limitations of the Ethereum blockchain. Polygon does this by creating an ecosystem of different scaling solutions and allowing them to integrate with each other easily. UniSwap is a popular decentralized exchange (DEX) that is one of many applications that run on the Polygon network.
How does Polygon work?
The Ethereum blockchain is like a busy highway with cars as transactions, on top of that, there are also expensive tolls. Scaling solutions act as new highways constructed with extra lanes with significantly lower tolls. Rather than providing a simple scaling solution like its predecessors, Polygon aims to offer multiple scaling solution frameworks. Polygon PoS and Polygon Hermez are two scaling solutions available in the Polygon ecosystem. The Polygon software development kit is another service offered that allows Ethereum-compatible dApps to be built on the MATIC network.
Polygon’s main scaling solution, PoS Chain, operates on a Proof of Stake consensus mechanism, which comprises validators and delegators.
Did You Know?
The explosive growth of Bitcoin has also led to scalability issues. The Lighting Network is a scaling solution that is used on the Bitcoin network to significantly lower costs and accelerate transaction processing times. It is also being trialled on the Litecoin network.
Validators
Validators are nodes on the Polygon network that earn rewards by verifying transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain. Validators will need to lock up MATIC tokens as collateral through staking. The blockchain protocol automatically selects validators using an algorithm. The larger the amount of MATIC staked, the higher chance of being selected. Any malicious attempts or errors can result in validators losing their staked MATIC, which helps incentivise good behaviour and high-quality performance.
Delegators
Using a consensus mechanism known as Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), delegators can stake MATIC through a validator of their choice without having to run a validator node. Delegators are also able to re-delegate their tokens with other validators. Delegators earn a percentage of rewards from their validator’s pool. Sharing rewards also means sharing the risk. For the interest of the network and your staked MATIC, delegators are encouraged to select validators that are behaving well.
Polygon Bridge
The Polygon Bridge is made up of the PoS bridge and the Plasma bridge. A bridge in crypto refers to a connection between two blockchains that facilitates the transfer of assets. Both the PoS Bridge and the Plasma Bridge operate as two-way bridges that can transfer assets between Ethereum and Polygon.
The Plasma Bridge is often used by developers, as it offers increased security. However, there is a drawback, namely the long withdrawal timeframes of up to seven days. The PoS Bridge is secured by the PoS consensus and offers quicker withdrawal times and supports a wider range of assets.
Sidechains vs rollups
Polygon currently has both a sidechain and rollup scaling solution, Polygon PoS and Polygon Hermez respectively. Sidechains are independent blockchains that operate very similarly to Ethereum, while rollups are built on top of Ethereum, functioning as an extension of Ethereum. Sidechains have their own consensus mechanism and are also responsible for their own security, whereas rollups are secured by Ethereum. Being a larger network, Ethereum is seen as more secure against 51% attacks.
Rollups help scaling by executing transactions outside of the main network, bundling them up, and adding them back into the main network. Similar to saving space on a computer by compressing files into zip folders. Optimistic and ZK rollup solutions offer different levels of security and functionality.
It’s worth noting that sidechains and rollups are still very new technologies, new versions are constantly being developed that tackle existing problems. Both sidechains and rollups have their benefits and drawbacks. For instance, side chains are flexible and offer lower fees, but rollups offer more security, so it largely depends on what developers want to prioritise.
Key Takeaway
Generally speaking, there isn’t one best scaling solution. Most proposed solutions excel in different areas and are better suited to certain applications. Sidechains are generally more flexible and have lower fees, but rollups have better security.
PoS chain
Polygon PoS chain is a sidechain that operates independently from the Ethereum blockchain and uses a separate consensus mechanism. As the name suggests, the PoS chain uses a Proof of Stake consensus mechanism. Polygon PoS chain operates using a blend of PoS chain and Plasma chain technology to help secure the network. The PoS chain is also Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatible, allowing Ethereum developers to easily migrate smart contracts.
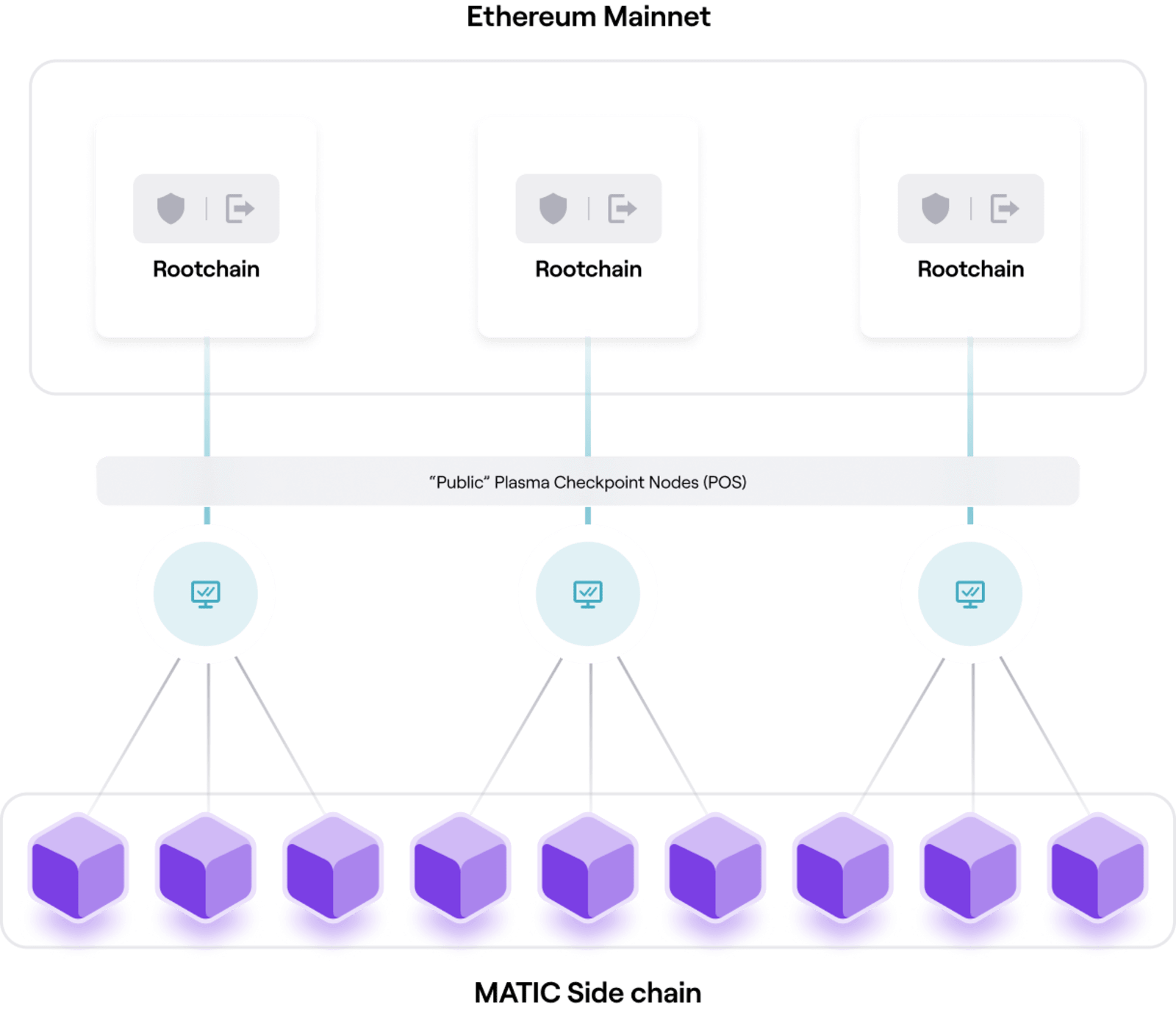
Figure 2 – Polygon PoS infrastructure
Plasma chain
Plasma is a framework proposed by Joseph Poon and Vitalik Buterin. Plasma technology uses Merkle trees to create smaller copies of the main blockchain that processes transactions. Each block of transactions contains a unique identifier, these identifiers are also known as state transactions. Polygon plasma chains aggregate all the state transactions and periodically transfers them to the main chain as a single block. Like washing clothes, it would be more efficient and cost-effective to use the washing machine for multiple clothes, instead of one shirt.
Network participants can challenge invalid transactions by submitting fraud proofs, which contain evidence that a state transaction is invalid.
Optimistic rollups
Polygon is developing frameworks compatible with scaling solutions. Optimistic rollups are a scaling solution that functions similarly to Plasma. However, transactional data are stored on the mainchain, allowing Ethereum nodes to verify transactions. Optimistic rollups assume that a transaction is valid until it is challenged. Like Plasma, Optimistic rollups use fraud proofs to settle disputes on the blockchain. However, the time it takes to settle a dispute can take days. Arbitrum is a Layer 2 scaling solution that uses optimistic rollups. Polygon Nightfall is a similar scaling solution that is currently in development.
ZK-Rollups
Polygon currently has a live framework called Hermez which uses Zero-Knowledge rollups (ZK-Rollups). State transaction batches are submitted to the main network alongside a validity proof, this removes the need for dispute resolutions, making the solution faster than Optimistic rollups. One downside to ZK-Rollups is that validity proofs use a lot of computational power.
Interesting Fact
Zero-knowledge proofs are also utilised in the privacy coin, ZCash.
Why is Polygon important?
Polygon solves many problems on the Ethereum blockchain, including low throughput, high gas and transaction fees, and difficulty with development. One of Polygon’s main attractions is how easy it is to build on their blockchain. On top of that Polygon provides options with different scaling solution frameworks that fits best with their project. You can think of Polygon as the blockchain equivalent of website building tools such as WordPress.
What is MATIC used for?
MATIC is the native cryptocurrency of the Polygon network. MATIC can be used to pay for network fees and also acts as a governance token. It can also be used for staking.
How to buy MATIC
You can buy MATIC from most large crypto exchanges. Swyftx is a reliable crypto exchange in Australia and New Zealand where users can buy MATIC with low fees and store it in their personal crypto wallet.
Summary
Polygon prides itself as Ethereum’s internet of blockchains, aiming to create an ecosystem of interoperable scaling solutions. Polygon’s main network features high throughput, low fees, and supports the Ethereum Virtual Machine, making it attractive for developers to build on. The Polygon team plans to provide even more scaling solution options in the future, including Optimistic Rollups, Standalone Chains, and more.
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.
