Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies hold the potential to function as truly peer-to-peer and compete against fiat currencies in the traditional sense. But the current state of blockchain technology is limited by a significant problem — scalability. Bitcoin transactions can be slow and expensive. The Bitcoin Lightning Network, however, promises to deliver instantaneous, nearly fee-free Bitcoin transactions. This guide will explain what the Lightning network is, how it works and why it’s important for the future of Bitcoin.
What is the lightning network?
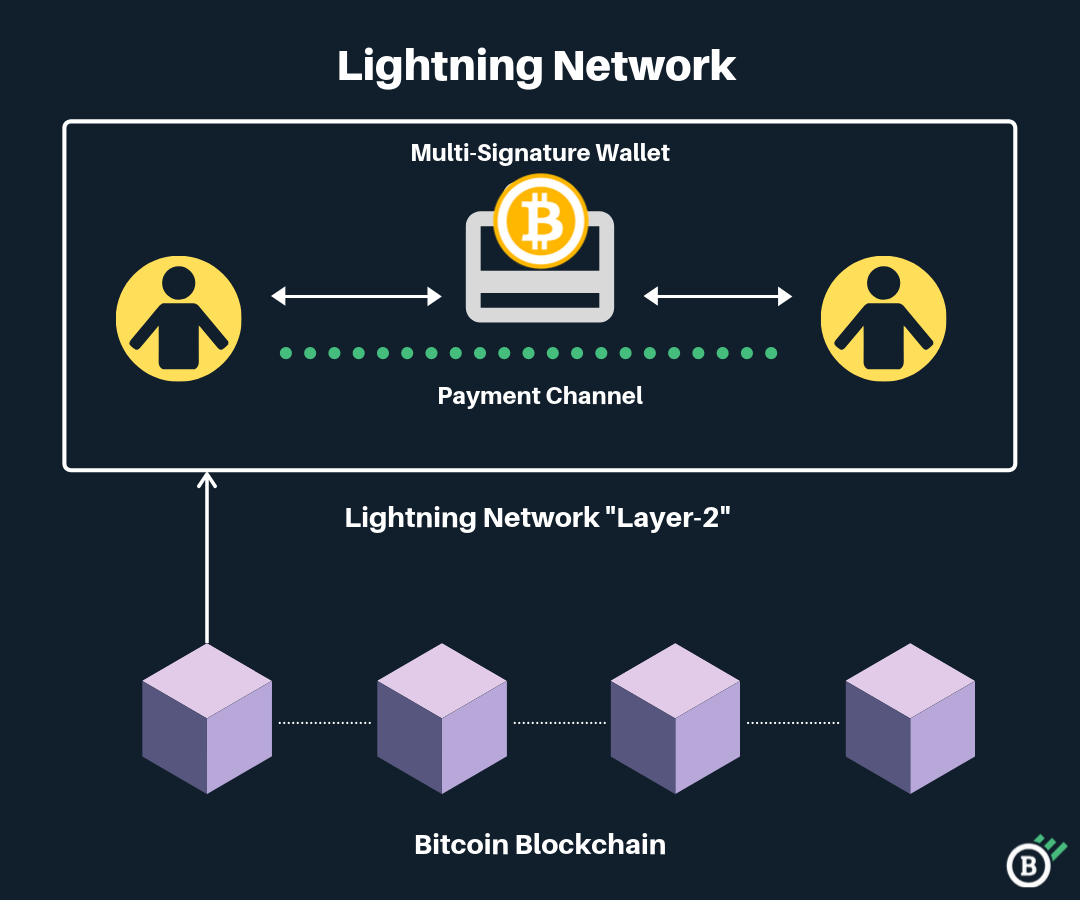
The Bitcoin Lightning Network is a scaling solution designed to allow Bitcoin users to send near-instant transactions between one another, accelerating transaction processing times, and significantly lowering the cost of sending transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain. The Lightning Network works by taking transactions off-chain, eliminating congestion on the Bitcoin network.
First proposed in 2015, the Lightning Network is designed to allow Bitcoin to reach the same level of transactions per second (TPS) as major credit card or payment processors I.e. Visa. Rather than process all Bitcoin transactions on the BTC blockchain, the Lightning Network creates a second layer above the Bitcoin blockchain, which consists of payment channels between two parties.
Transactions executed via these payment channels are processed in a different way than transactions on the main Bitcoin blockchain. These lightning transactions are only recorded to the main Bitcoin blockchain when a lightning network channel is closed. Using payment channels, two parties are able to instantly send Bitcoin to each other without waiting for confirmation from the Bitcoin main chain.
Key Takeaway
The Bitcoin Lightning Network allows people to send Bitcoin instantly with next to no fees by moving transactions off the main blockchain and on to a payment channel between the two parties.
What problem does the lightning network solve?
As the popularity of Bitcoin increases, so too does the number of transactions that must be processed by the Bitcoin network and added to the Bitcoin blockchain. Bitcoin maintains a distributed ledger, which is validated and secured by thousands of nodes (computers) that each hold a copy of the ledger and work together to keep it up to date.
The decentralized nature of Bitcoin means it operates without a centralized authority. This means it is virtually impossible to hack and is self-policing. The same features that make Bitcoin accessible and decentralized. however, currently create a bottleneck that prevents Bitcoin from processing transactions at scale.
Bitcoin’s scalability issue
Each transaction made on the Bitcoin network is confirmed by nodes within the network and then bundled into blocks and committed to its blockchain. This process is known as mining. New blocks are added to the BTC blockchain every 10 minutes — each block can contain roughly 1,800 to 2,000 transactions.
At peak efficiency, the Bitcoin network can perform at 6-7 transactions per second (TPS). Bitcoin transactions are much slower than when compared to traditional payment processors such as Visa, which has been demonstrated to be capable of anywhere between 1,700 and 24,000 TPS.
The slow speed at which Bitcoin is able to execute transactions also contributes to high transaction fees when the network is congested. Miners will prioritise transactions with higher transaction fees first, which causes Bitcoin transaction fees to skyrocket.
Did You Know?
The Bitcoin blockchain network can only process 6-7 TPS, which is very low when compared to credit card and payment processing giant, Visa, which can process between 1,700 and 24,000 TPS. Solana is said to be an industry leader as it can reportedly process up to 65,000 TPS.
How does the lightning network work?
The Lightning Network may seem complicated but makes sense when considered in a practical manner.
Example:
Jen, a lightning network user, wants to send Bitcoin to her co-worker, Tom. Rather than create a new transaction on the Bitcoin main chain, Jen is able to create a payment channel on the Lightning Network with Tom.
Transactions made between Jen and Tom are executed instantly, creating a direct channel between the two parties.
Additionally, if Tom decides to buy a coffee with Bitcoin at a local coffee shop and creates a payment channel with that coffee shop, Jen will then be able to purchase coffee through the same payment channel, as all parties are connected.
The same logic as the example above can be applied to any party that transacts with the coffee shop, creating an expanding web of transactions that provides near-instant execution time with minimal fees.
In order to create this web of payment channels, the Lightning Network uses smart contracts and multi-signature wallets. To create a payment channel, two parties initiate a funding transaction, and exchange two keys — one public, and one private. This allows the two parties to instantly transfer funds to one another.
When a payment channel is closed, data on the initial and final balance of the channel is broadcast to the main Bitcoin blockchain. The core premise of this decentralized network scaling solution is that once Lightning Network payment channels become widely adopted it won’t be necessary to create new channels to send funds to another party — by routing through multiple routes, the Lightning Network system will automatically find the most efficient route.
Disadvantages of the lightning work
A disadvantage of the Lightning Network, however, is that it operates as a layer on top of the Bitcoin blockchain and thus does not benefit from the same security as the main chain. Rather than facilitate instant payments of any size, the Lightning Network is designed to facilitate instant day-to-day small transfers and purchases — large transfers that require the security offered by the Bitcoin blockchain must still be executed on the main chain.
Lightning Network adoption has increased steadily since the 2017 launch of the solution, with multiple platforms and exchanges starting to integrate Lightning Network support. Live Lightning Network data trackers indicate a 200%+ increase in the number of nodes added to the Lightning Network from mid-2020 to end of 2021, with the total amount of payment channels doubling in the same time period.
How is the lightning network implemented?
While the Lightning Network currently holds almost $100 million in Bitcoin, it’s still under development — there are, as of yet, no streamlined frontend apps or software solutions with which casual Bitcoin users can create Lightning Network payment channels or make Lightning Network transactions.
Crypto exchanges supporting the network
Some cryptocurrency exchanges are beginning to support the lightning network. These exchanges allow their users to withdraw and send lightning network payments of Bitcoin quickly and with low fees. This is possible even when Bitcoin traffic is congested.
Why does the lightning network matter for Bitcoin users?
The Lightning Network is a work in progress, but it holds the potential to transform the way users interact with the Bitcoin blockchain. The Lightning Network, once live, operational, and accessible to casual users, will eliminate transaction waiting times. It will also mean significantly lower transaction fees, allowing Bitcoin to compete directly with traditional payment processors.
The successful launch of a consume-ready Lightning Network would allow users to purchase goods and services instantly with Bitcoin anywhere, at any time, without waiting for block confirmations. Other unique and promising applications of Lightning Network technology include cross-chain atomic swaps, which make it possible to instantly exchange value from one blockchain to another, such as instantly exchanging BTC for ETH without the need for an intermediary.
Summary
The Lightning Network is a layer-2 scaling solution that allows people to open payment channels between each other so send and receive Bitcoin quickly. This can then create a network of interconnected users. The Lightning Network aims to facilitate the instantaneous execution of Bitcoin transactions with minimal fees and once launched, holds the potential to transform Bitcoin into a cryptocurrency that can be used for day-to-day transactions.
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.