Amidst the noise of “disruptive” innovations and game-changers, one particular technology has generated the most buzz in recent years: blockchain technology. Blockchain is a type of technology that stores data in the form of blocks. Blockchain tech forms the backbone of Web 3.0 by providing an avenue for seamless transactions and a clearinghouse for all interactions on its network (i.e. data). It has the capacity to transform the financial services industry, charitable giving platforms, supply chain management, music streaming services, smart cities, and so much more. This guide will explain what blockchain is, how it started, how it works, and what the future of blockchain technology might look like.
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain is a shared, unchangeable record of all the transactions that happen within a network. This list of transactions is time-stamped and data-driven. The use of cryptography and hashing makes altering the blockchain network very difficult, if not impossible.
As a public ledger system, blockchains are decentralized and do not have a central authority. All of the financial information contained in crypto transactions are stored on the blockchain and distributed across all connected computers. A blockchain community consists of a network of computers or ‘nodes’ which each store a copy of the blockchain.
Assets tracked with blockchain technology can be tangible or intangible, from cash or houses to IP and branding. Almost any asset of value can be traded on the blockchain.
How did blockchain start?
Blockchain was originally designed by a person or group of people using the pseudonym, Satoshi Nakamoto. It was designed as a distributed ledger for verifying and recording transactions of Bitcoin – but has evolved to be much more. Intermittent failures in centralized databases vulnerable to cyberattacks led Nakamoto to develop blockchain technology. In 2008, Nakamoto published the Bitcoin whitepaper and developed a peer-to-peer digital currency, Bitcoin.
Blockchain technology has advanced rapidly since Bitcoin was first released. It’s suited for various industries, and digital currency is the most popular blockchain-based application. Blockchain has become the key to securely tracking and recording online transactions. From cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to logging land titles, blockchain has been used to solve many problems that were difficult or impossible before its invention.
How does blockchain work?
Creating blocks
Every blockchain starts with an initial block, called the “Genesis Block”, with every following block linked to the block immediately prior. The blockchain is secure because each block uses a cryptographic hash function to make it unique.
Key Takeaway
A blockchain is formed from a chain of blocks, each of which stores information. The exact information a block stores differs between blockchains. Bitcoin, as an example, contains information about the total BTC being transferred as well as details about the sender and receiver.
All transactions are recorded on the blockchain. When someone requests a transaction, the request is then broadcast to a network of nodes that will validate the transaction. The way transactions are validated is by getting the computers on the blockchain network to agree on the details of the transaction, by solving a mathematical puzzle. Once the transaction has been validated, the transaction is then combined with other transactions to create a new block. This block is then added to the chain of existing blocks.
This means you can’t delete any of the records – good or bad. If the ledger is public, every transaction carried out on blockchain technology can be seen by anyone on the network. It is transparent and doesn’t require international currency exchange fees or personal details that could be hacked or stolen.
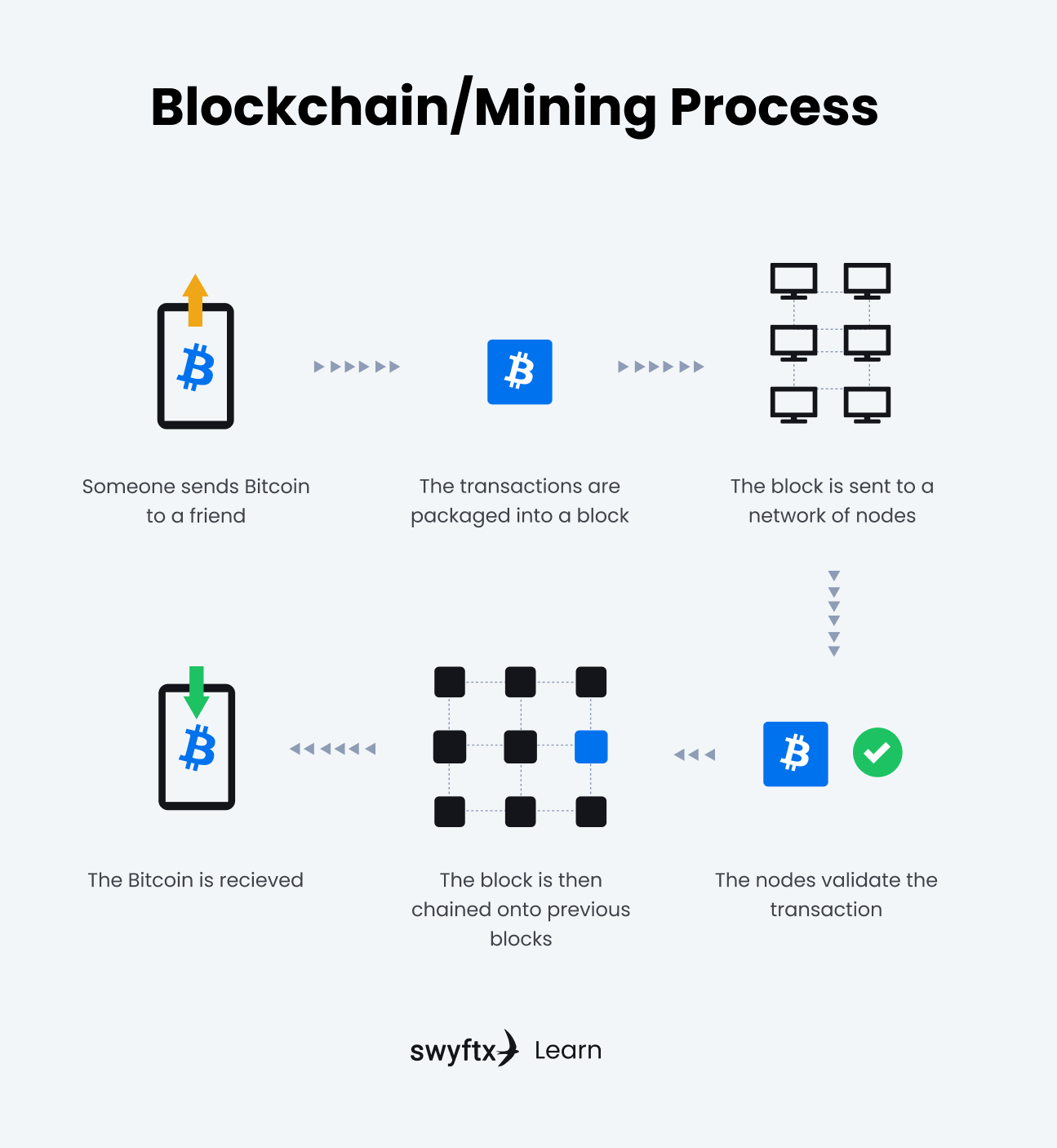
Figure 1 – Blockchain process explained
The core elements of blockchain technology
The core elements on which blockchain operates are its distributed ledger technology, consensus mechanisms, immutable records, and smart contracts.
Distributed ledger technology (DLT)
A distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a digitised, decentralized, and time-stamped series of records that are stored across multiple sites, countries, or institutions. The information in a distributed ledger is updated simultaneously across every copy held by participants on the network.
Using DLT means there’s no need for an intermediary or third-party provider to manage the exchange of information and trust between parties. When everyone in the chain has access to all of the source records, it’s a lot easier to verify identities and keep track of transactions.
Tip
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is, in essence, a global, digital library. Everyone with a membership card has a copy of every book, record, or piece of information in that library. And when any of that information is updated, those updates are transmitted across the entire library.
Consensus mechanism
Every blockchain network uses a consensus mechanism in order to verify and process transactions. Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are two of the most popular consensus mechanisms used on blockchains.
Immutable records
Immutable records, mean that the information on a blockchain network can’t be changed without re-writing all of the following blocks. The same way that a mason can’t change or switch out a piece of stone once additional layers have been added on top.
Every single transaction that occurs through smart contracts and payments are scrutinised by other nodes within that network to ensure their authenticity and validity.
Smart contracts
The interconnected nature of the blockchain allows for smart contract agreements that are automatically executed once their requirements are met, such as receiving payment or certifying a certain data point has been collected.
It’s an agreement set out in coded language through which two parties agree to perform or not perform some action. If the transaction takes place between known entities, smart contracts make it easier to verify the rules are upheld.
Smart contracts can be created for anything from property sales to car rentals, smart energy grids, and even employee contracts.
Examples of popular blockchains
There are numerous blockchain networks and platforms out there, but we’ll look at two of the most well-known: the Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchains.
The Bitcoin blockchain
The Bitcoin blockchain uses a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus algorithm. With Bitcoin’s blockchain network, every time someone sends BTC from one account to another the transaction is encoded into a block containing all of the information about the transaction, including the time and date of transfer, as well as the sending and receiving addresses. This block is then linked to a previous block that has been encoded with other transactions.
The Ethereum blockchain
Ethereum also currently uses a PoW consensus algorithm but is in the process of transitioning to Proof of Stake (PoS). Ethereum is an open-source blockchain, which features its own cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH). It works in a similar way to Bitcoin and other blockchains, but it is versatile and has many more applications. It allows developers to write smart contracts and develop decentralized applications (dApps) that operate on the blockchain. This means transactions and apps can be encoded into blocks and stored permanently, without risk of being deleted or tampered with by unauthorised parties.
Blockchain benefits
Blockchain provides many advantages over conventional methods of transactions and record-keeping, such as security, speed, and cost-effectiveness.
Security
A major benefit of blockchain technology is its security. Because there is no central location for the blockchain network, if a hacker wanted to break into a smart contract or smart property, they would have to gain access to every computer in the chain at the same time. This makes it extremely unlikely that any cybercriminal will ever penetrate your smart contract or smart property.
Speed
The blockchain network is able to process transactions in real-time, which is why many believe it will become an integral part of the future financial system. In fact, some believe that blockchain could be used to challenge existing institutions like SWIFT.
Cost-effectiveness
Blockchain could potentially eliminate the need for banks and other third parties that often add significant costs to the consumer. The blockchain model is designed in a way that reduces or eliminates the need for intermediaries, which not only saves time and money but also prevents delays in processes.
Blockchain has already changed the financial industry by providing faster, cheaper, and more secure transactions. However, this technology will likely be applied to or expanded upon in many other areas of personal and business activity in the future, including healthcare, food and agriculture, logistics, and the public sector.
Key Takeaway
Blockchain is an incredibly fast, cheap, secure, and versatile technology. It can be applied to recording financial transactions, storing medical records, tracking the flow of goods, executing binding agreements, tracking the ownership or origin of artwork, storing personal credit records, verifying payments through a supply chain, and much more.
Blockchain and the future
Blockchain technology is increasingly heralded as the “fifth evolution” of computing. Originally, blockchain was just a word used to describe how data would be structured and shared. Now, blockchain is a fully-fledged technology and a new way to exchange money, data, and anything of value. Blockchain enables us to share information with anyone without the risk that it will be used for other purposes or changed in an undesirable way.
Blockchain technology is an exciting prospect for individuals looking to invest in cryptocurrency as well as businesses hoping to improve their efficiency and reduce costs. As blockchain technology advances, the demand for people with expert knowledge of this field is sure to increase.
Summary
Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that stores data in the form of blocks. Blockchain has the capacity to transform financial services, healthcare, music streaming, food and agriculture, and so much more. If you want to learn more about smart contracts, consensus mechanisms, or anything else blockchain or crypto-related, there are lots of great resources on Swyftx Learn.
Next lesson
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.


 Article read
Article read