
The world of cryptocurrency is vast and exciting. But its fast-paced environment can be a bit overwhelming when you are first getting started. Whether you want to begin building your very own crypto portfolio, or just learn about how everything works, this guide will run through the basics to get you off the ground floor.
What is cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency is a type of digital asset or currency that is secured using cryptography, a method of encrypting information. This security makes it extremely difficult to counterfeit or spend the same cryptocurrency twice. Bitcoin is the most well-known cryptocurrency, but there are now more than 20,000 others in circulation.
Most cryptocurrencies are built on blockchain technology, which is a distributed ledger maintained by a network of computers around the world. A defining characteristic of a cryptocurrency is that it is usually not issued by a central authority, such as banks or governments, meaning that they are resistant, but not immune, to government manipulation and interference.
Blockchain technology is the core of decentralisation, and is one of cryptocurrency’s defining characteristics.
Key Takeaway
The fundamentals of cryptocurrency work a bit like storing valuables in a digital safe. Your crypto assets are the valuables you’re protecting, while cryptography acts as the safe’s unique PIN, ensuring only the rightful owner can access them. Meanwhile, the blockchain works like a public, permanent logbook that records every time the safe is used. This logbook makes it easy for everyone to see if something unusual happens.
How did cryptocurrency start?
In 2009, in the wake of the global financial crisis, an anonymous developer – or group of developers – known as Satoshi Nakamoto created Bitcoin, the world’s first cryptocurrency. Nakamoto’s goal was to build a global, decentralised digital currency, free from the control of traditional banks and governments, whose failures had contributed to the 2008 economic recession.
Did You Know?
While Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency, it was not the first blockchain. In fact, the concept of blockchains had been around for nearly two decades before Bitcoin was introduced to the world. In 1991, two scientists working in the United States developed an early version of blockchain technology through a system designed to securely time-stamp digital documents. Satoshi built on this idea by introducing an economic incentive system among other innovations — and Bitcoin was born.
A brief history of cryptocurrency
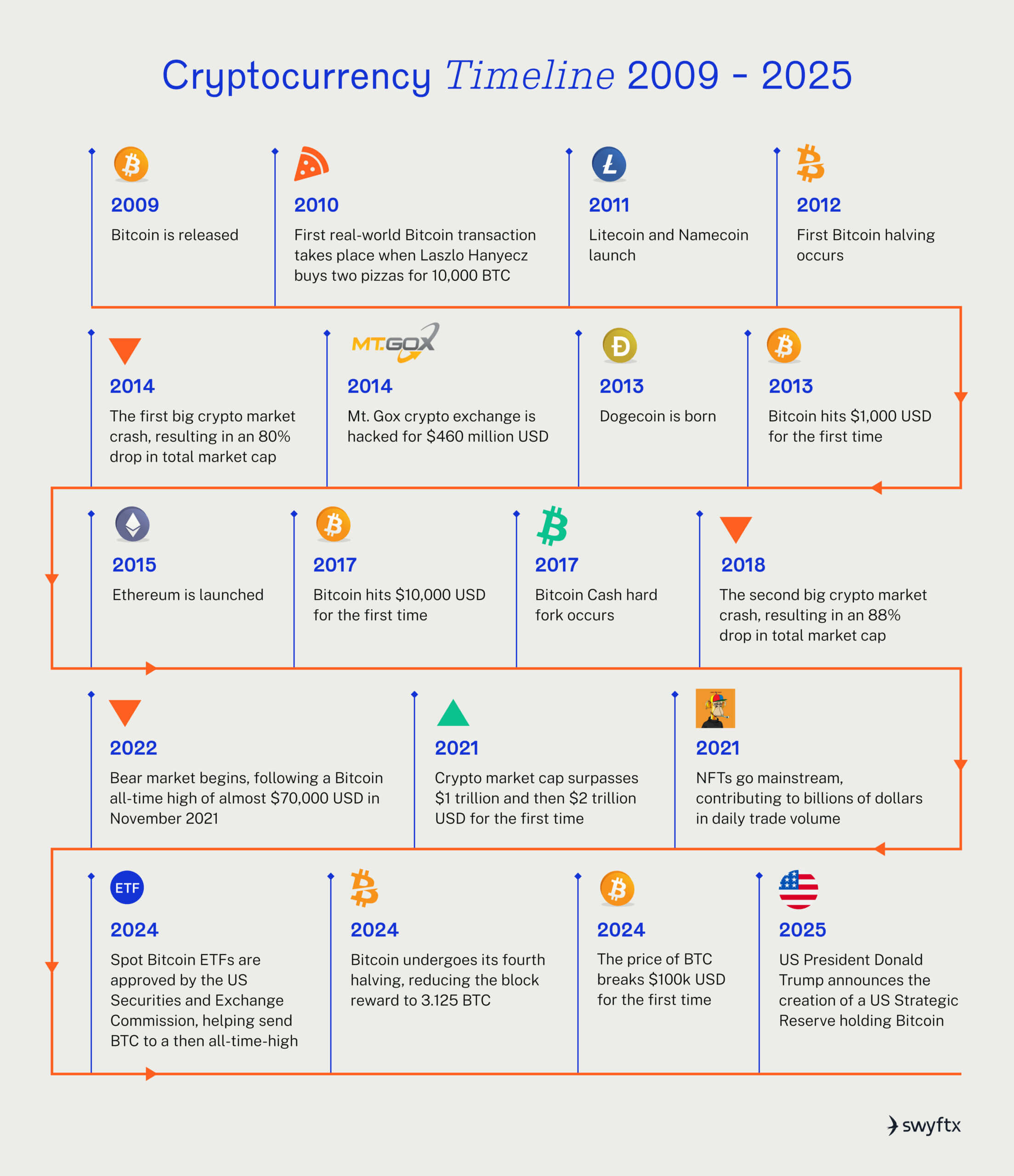
Cryptocurrency timeline from 2009 to 2025
Why are cryptocurrencies becoming popular?
Crypto is growing in popularity as an investment, for its low transaction costs, and for its potential to shape the future of financial technology.
Cryptocurrency transactions can be cheap and efficient
Because crypto doesn’t rely on a middle party to settle transactions – like a bank, or stockbroker – using it can be a lot cheaper. For example, sending money internationally can take days and incur large fees via traditional systems.
However, using crypto to send money abroad can cost less than a cent and arrive within seconds.
Crypto is seen as the future
Cryptocurrency technology has been touted as the future of the economy. While this is a broad and ambitious claim, digital currencies have already cemented their role in the current financial system. You can buy Bitcoin on the stock exchange, invest in crypto through your super fund and use stablecoins to move money instantly across borders.
Cryptocurrency projects have evolved far beyond simple payments and are now used across finance, cloud storage, gaming, trading, art collecting, contracts, documentation, and even voting.
As technology continues to advance, many believe cryptocurrency’s role in everyday life will grow alongside it.
Potential as an investment
Cryptocurrency has become a popular tool for investors to diversify their portfolios. Since its inception, Bitcoin has outperformed most major stock indices and has become more prominent among retirement funds like crypto SMSFs. In fact, estimates from the ATO show that over $1.7 billion AUD worth of crypto is held in self-managed super funds as of December 2024.
Additionally, cryptocurrency exchanges typically offer low investment minimums and around-the-clock trading hours, providing more accessibility than many traditional markets.
Pop Quiz
Cryptocurrencies are built on decentralized networks and based on blockchain technology.
Some examples of popular digital currencies
The cryptocurrency market is full of exciting projects. There are a lot of different cryptocurrency use cases. Many of them have a specific utility and others aim to solve a particular problem, which we will touch on in the next lesson.
Bitcoin was the first – and remains by far the most famous – digital asset on the market.
Ethereum is another leading cryptocurrency project, often credited with birthing decentralised finance (DeFi).
Tether USD (USDT) is a prominent stablecoin, which means the cryptocurrency’s value is tied to that of the US Dollar. It avoids the price swings of most digital currencies while keeping the benefits of fast, low-cost transactions.
Dogecoin, originally created as a joke, evolved into a cultural phenomenon that sparked the ‘memecoin’ sub-sector of cryptocurrency.
Why does the price of crypto change?
The crypto market has a lot of inherent value, but it is also heavily driven by speculation, similar in some ways to the stock market and real estate.
For example, in the stock market, investors and traders try to predict what businesses like Apple and Tesla will be worth in the future. They look at factors like company profits, competition, government rules and how popular the company’s products or services are.
Cryptocurrencies can be valued in a similar way. Investors use a range of information – such as how many people use the crypto, future technological upgrades or potential partnerships – to decide if a project is worth buying.
Just like in most markets, supply and demand reigns supreme. If more people want to buy a cryptocurrency than sell it, the price will usually go up.
Important to Remember
Crypto is often associated with major market crashes – and while volatility is real, this perception is often shaped by timing. Many first-time investors enter at market peaks, when media coverage and social hype are at their highest.
But just as crypto can crash hard, it can also soar. In 2018–19, the overall market fell by around 88%. Yet by 2021, it had climbed roughly 2,500% from those lows. Financial markets often move in a cyclical fashion, and cryptocurrency is no different.
How do I buy cryptocurrency?
The easiest way to buy and sell crypto is to use a cryptocurrency exchange, such as Swyftx. There you will be able to deposit fiat currency and buy the cryptocurrencies of your choice, quickly and affordably. You can then store your cryptocurrency on the exchange to sell at a later point, or you can transfer it to a software or hardware wallet if you plan to hold it long-term.
Summary
The growing world of cryptocurrency is full of opportunity. From humble beginnings in 2009 — when Bitcoin was little more than an idea — crypto has evolved into a trillion-dollar market.
The fast-changing landscape has the potential to reshape industries, from finance to supply chain to digital content.
Next lesson
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.

 Course rewarded
Course rewarded
 Article read
Article read



