The global economy is a complex, intertwined system comprising governments, businesses and individuals.
The study of macroeconomics interrogates this large-scale economic sphere to understand the factors that shape the worldwide financial system.
Macroeconomics is typically considered from a global or national lens — analysing and reacting to things like Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation and unemployment.
The macroeconomic environment can have a massive impact on all financial markets, including crypto.
What is macroeconomics?
Macroeconomics is the analysis of an entire economy’s activity, typically by diving into national or global trends.
This can look quite different from other common forms of measuring markets. For example, an investor might investigate the token allocation of a new crypto project to examine its supply and demand metrics.
Or, traders might track the RSI momentum of a certain digital asset as part of a technical analysis strategy.
These research methods differ from macroeconomics as they are usually restricted to a specific market (cryptocurrency) or asset (like Bitcoin).

Did You Know?
The paradox of thrift is a macroeconomic theory that suggests, on a microeconomic level, individual households saving is good for the economy, as it can improve loan liquidity and reduce the government’s spending burden. However, on a macroeconomic level, too many people saving (and thus not spending) can ultimately cause an economic slowdown.
What are the key macroeconomic concepts?
There are many macroeconomic indicators that can have a major impact on the global economy and the markets that comprise it. These factors are often heavily linked, with movements in one metric causing a ripple effect across a nation’s economy.
We will dive further into some of these as we move forward in the series.
Inflation rate
Inflation is one of the most important tools when measuring an economy. This metric determines how much the price of goods and services increases over a given timeframe. Too much inflation — typically caused by increased spending or production costs — can result in financial stress for an economy.
On the flipside, deflation suggests economic production and activity may be too low, which could impact employment levels.
Unemployment rate
The unemployment rate measures the number of people within a country without a job, but who are on the hunt for one. A high unemployment rate suggests an economy in recession, while extremely low unemployment can result in unsustainable inflation.
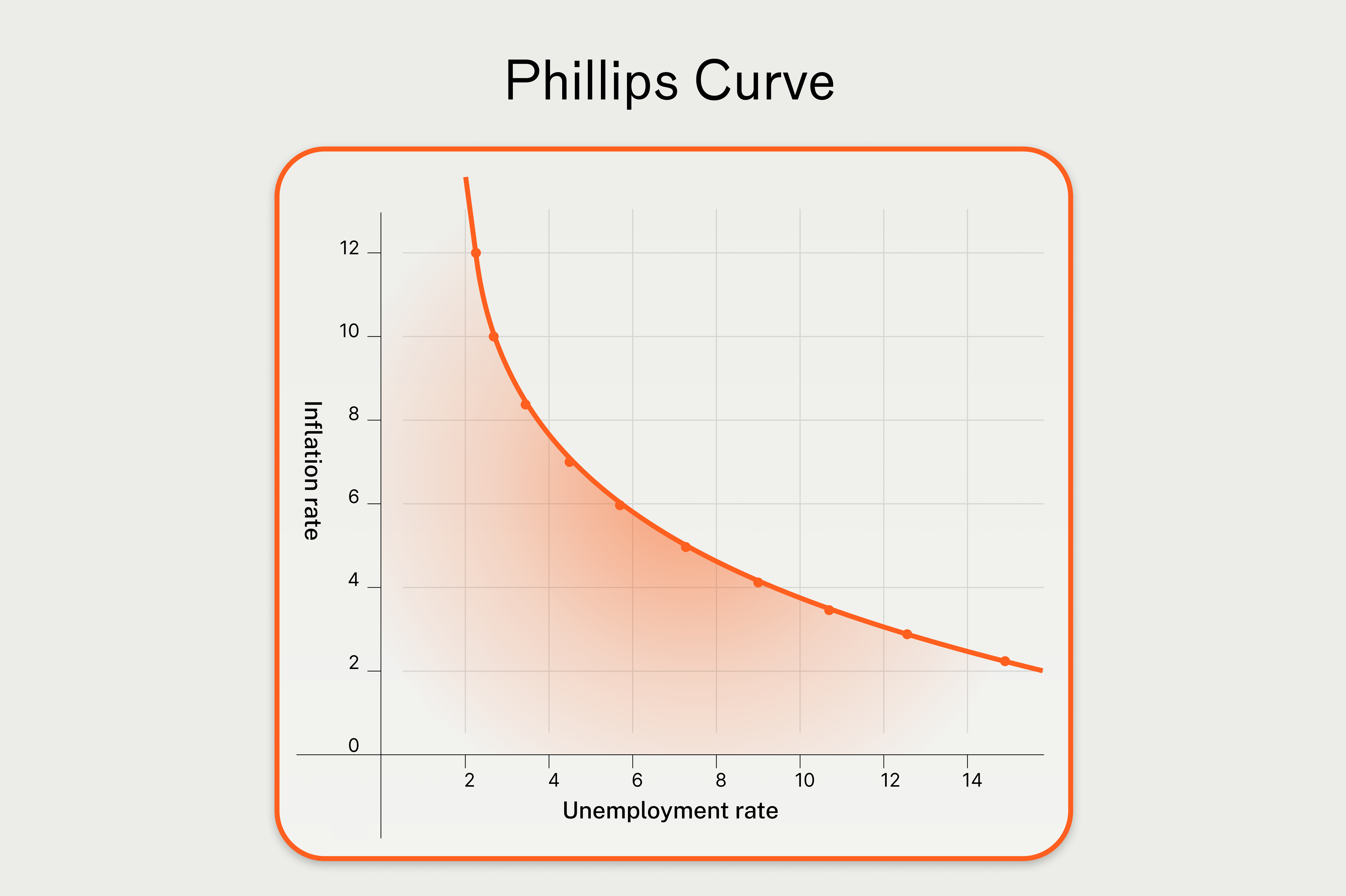
Economic output
The economic output of a nation is typically measured via Gross Domestic Product (GDP). This indicator measures the total value of goods and services created by a country within a given period. An increasing GDP can suggest economic health and growth, while stagnating or falling GDP figures may indicate instability.
Fiscal policy
A government or central bank (like the Reserve Bank of Australia) can implement laws to manipulate the macroeconomy. For example, following the significant market drawback and loss of jobs following Covid-19 lockdowns, the RBA decreased interest rates to stimulate spending and productivity.
Geopolitical conflict
The geopolitical landscape is constantly shifting and can place major stressors on the global economy. For example, trade wars and tariffs can reduce a country’s GDP, as the increased cost of imports may cause a drop in demand.
Key Takeaway
Remember, macroeconomic factors are often engaged in a perpetual game of tug-o-war. For example, imagine a geopolitical conflict that causes oil prices to surge, leading to higher inflation. This reduces consumer spending, decreases GDP, and raises unemployment. In response, the RBA lowers interest rates to counteract the economic downturn and encourage growth.

How can macroeconomics influence the price of crypto?
The macroeconomy considers massive financial factors like how many people are in work, the price of your weekly grocery shop and how expensive it is to borrow money. So it’s no wonder that macroeconomics plays a huge role in the movements of the crypto market.
From a really broad sense, macroeconomics helps gauge the position of the global economy — especially when applied to financial powerhouses like the United States and China.
So, if macroeconomic figures are trending toward a recession, investor sentiment might sour, leading to a market pullback. Economic downturns mean less money floating around, which in turn means less money for risky, growth assets like crypto.
Individual macroeconomic factors can have a massive flow-on effect on the crypto market too.
For example, a low-interest rate policy in the United States means instruments such as Treasury bonds and high-interest saving accounts may yield less than desired for institutions. This could make crypto and other riskier investments a more attractive value proposition.
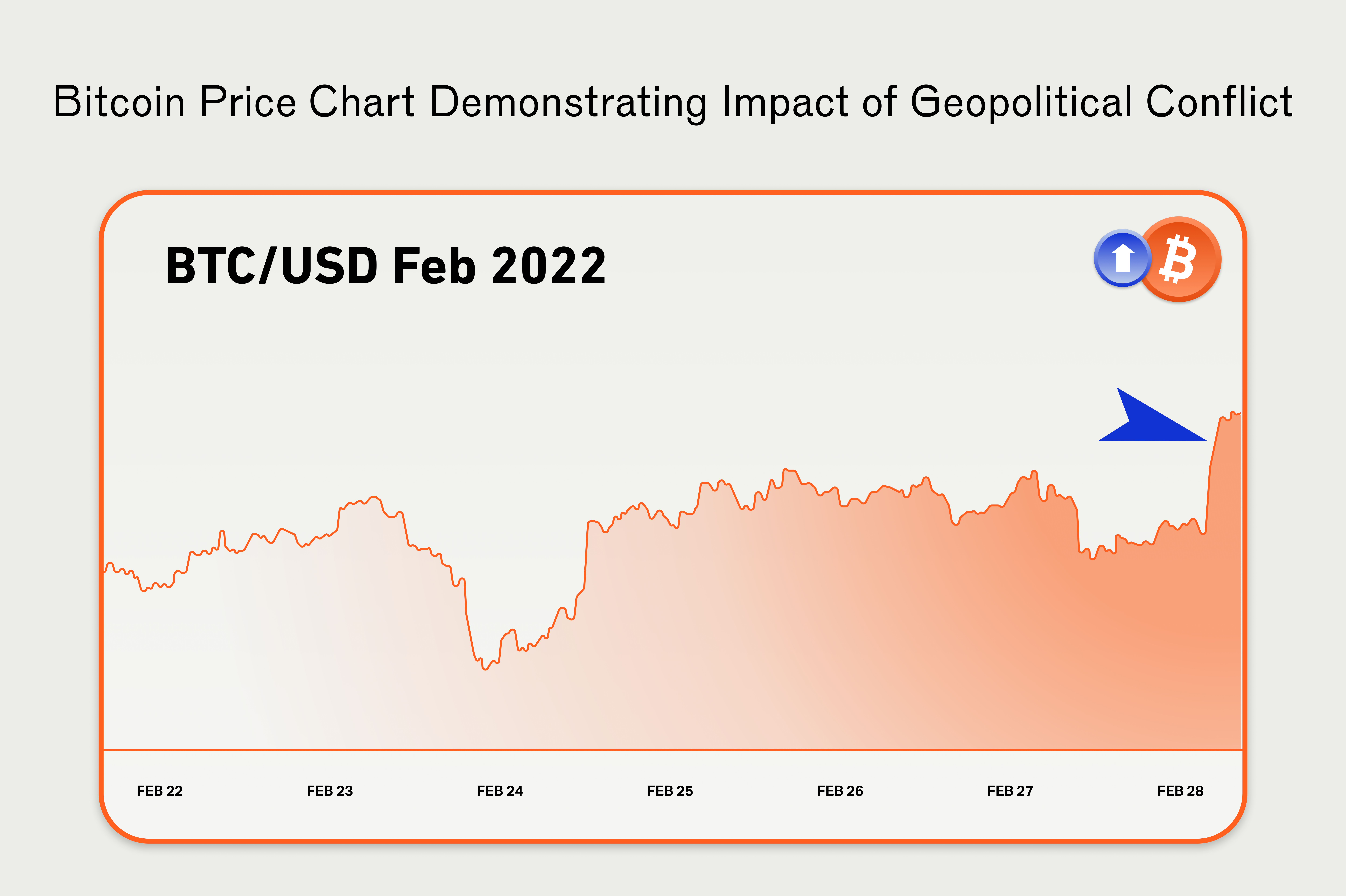
Or, businesses and individuals within a country may turn to cryptocurrency in the event of significant inflation. The market has experienced this before, following the Russian Ruble’s collapse due to geopolitical sanctions in 2022.
To protect the value of their holdings, Russians poured billions of USD into Bitcoin, causing BTC’s price to spike 20% within a handful of days.
Summary
The study of macroeconomics is a popular tool used by investors, economists and governments to understand the global economy. These metrics can provide unique insights into how the financial system is working, and help investors forecast where it may be headed in the near future.
Understanding macroeconomics is vital for anyone participating in a financial market, but it is not a silver bullet. Including analysis of specific fundamental and technical details can help investors craft a well-rounded trading strategy.
Next lesson
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.


 Article read
Article read