
Key Takeaways
- Decentralised finance (DeFi) enables financial activities like lending and trading on blockchain without traditional banks.
- Ethereum is the dominant platform for major DeFi projects like Uniswap and Aave.
- The future is bright for DeFi with strong fundamentals, product-market fit and the unlocking of Bitcoin collateral.
What Is Decentralised Finance (DeFi)?
Decentralised finance (DeFi) is a term that describes a suite of crypto projects that are decentralising financial services. It is a blockchain-based system that allows users to engage in traditional banking activities like lending, borrowing, and trading without relying on centralised intermediaries like banks. It offers more transparency, accessibility, and control over personal finances, empowering individuals to manage their assets directly.
Why DeFi?
The current financial system relies on institutions and banks to serve as its trust layer. With the help of law enforcement, these trusted intermediaries help keep the financial system working. For doing so, we pay them fees and agree to terms about how we use these intermediaries’ services.
With DeFi, there’s no need to trust a middleman. DeFi describes a suite of crypto projects that use a blend of cryptography, smart contracts and blockchain technology to keep their platforms regulated instead of a central body.
The total value locked (TVL) in all DeFi protocols hit a record high of $240 billion (USD) in December 2021. In the years since, like many crypto prices, TVL has steadily declined. As of August 2024, TVL is around $100 billion.
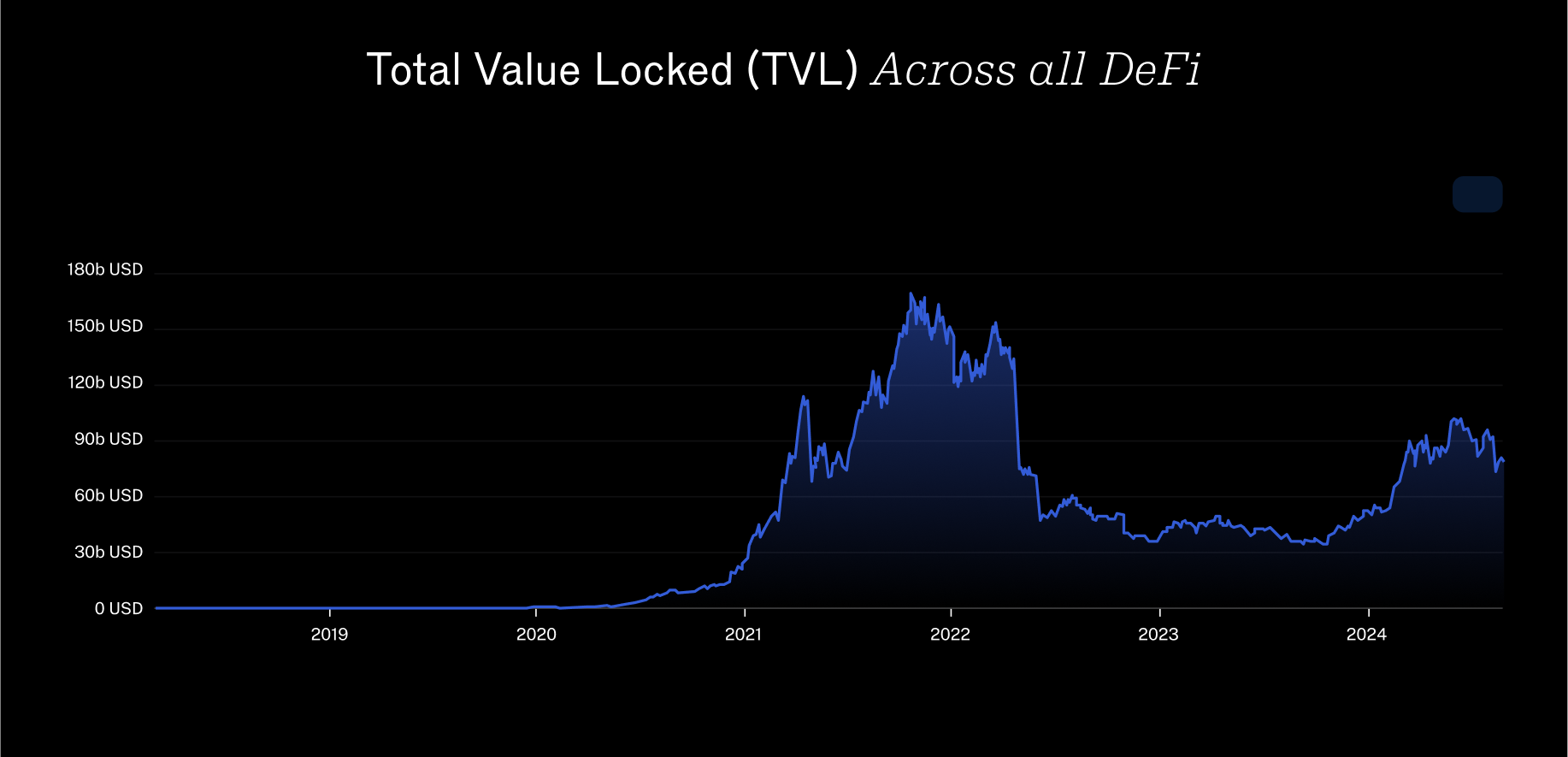
TVL across all DeFi (Source: DeFiLlama)
What Are DeFi Protocols?
There are three main types of DeFi protocols.
1. Decentralised Exchanges
Projects like Uniswap and Jupiter allow users to trade cryptocurrencies without relying on a central authority, using smart contracts to facilitate transactions.
2. Lending and Borrowing Protocols
Projects like Aave and Kamino enable users to lend their crypto assets to others or borrow against them, often earning interest or paying fees in a decentralised, trustless manner.
3. Staking Protocols
Projects like Lido and Jito enable users to lock up their crypto assets in a blockchain network to support operations like transaction validation, earning rewards in return for their contribution to network security.
Over the years, other DeFi projects have attempted to mimic other aspects of traditional finance (e.g. insurance, asset management, risk management). These largely remain experimental and are auxiliary to the three categories listed above.
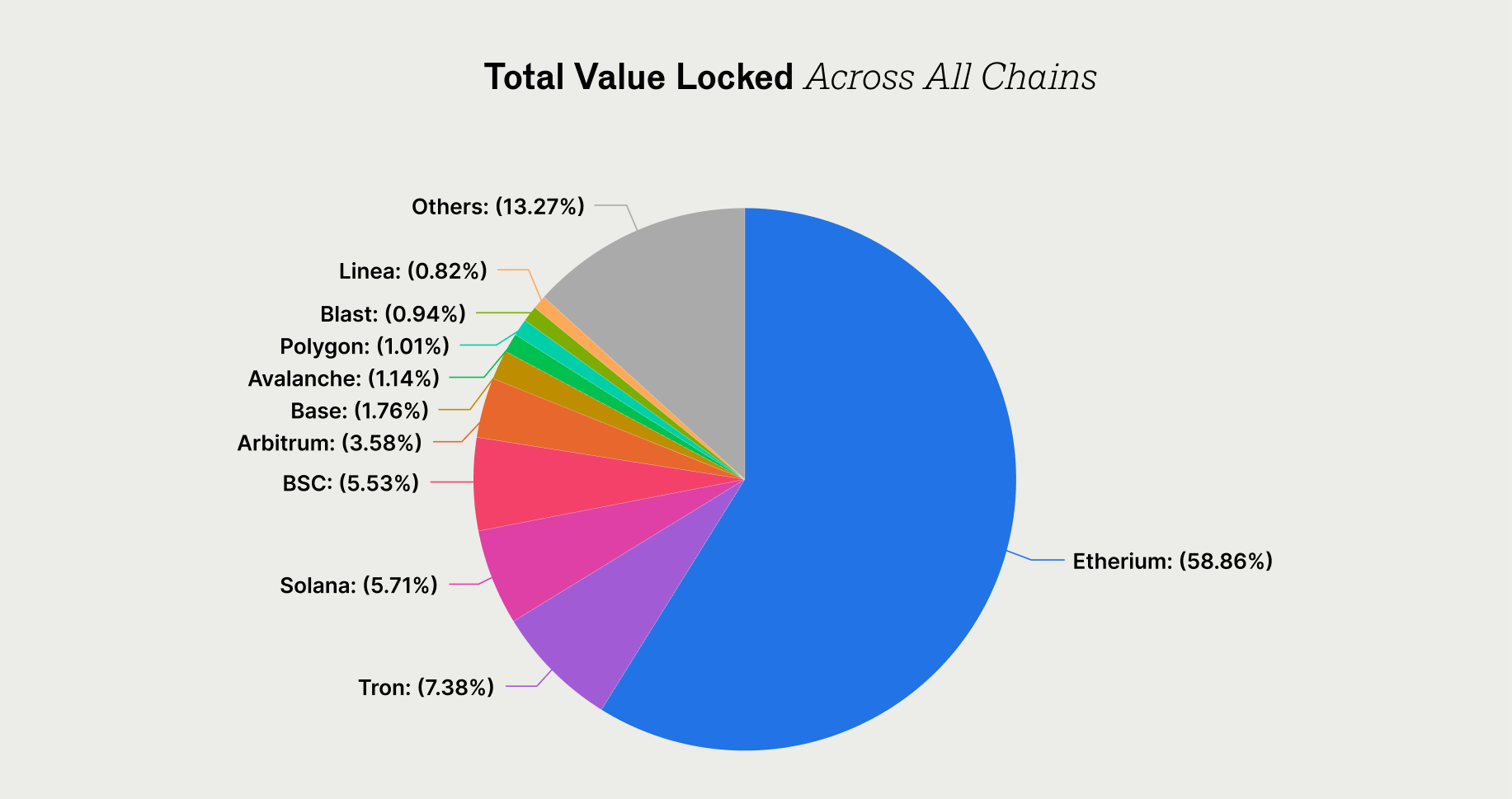
DeFi is predominantly on the Ethereum network (Source: DefiLlama)
Future Catalysts
DeFi has moved beyond its speculation phase, with projects now demonstrating product-market fit. Combined with the fact that most major DeFi projects are fully vested (i.e. all tokens unlocked), their tokens face relatively less sell-side pressure than the hundreds of newer projects.
DeFi represents a real use case for blockchains with genuine yields, providing strong fundamental reasons why it should perform well this cycle. Users can be rewarded in multiple ways, either by utilising the protocols themselves and earning fees or by holding the tokens of strong market leaders in the space.
Another potential source of major growth for DeFi is layer-two solutions on the Bitcoin network. Unlocking the collateral of the largest cryptocurrency could unleash a new wave of DeFi innovation, leading to both copycat products and the implementation of new ideas.
Key DeFi Players on Ethereum
Uniswap (UNI)
Uniswap is the largest decentralised exchange by 24-hour transaction volume, as per CoinGecko. In fact, it is only surpassed in volume by a few of the biggest centralised exchanges.
Uniswap allows people to trade crypto assets without a central authority, operating in a trustless manner. Beyond enabling trades, it allows users to deposit funds to facilitate these transactions. Depositors earn fees for providing the liquidity that powers the exchange.
Uniswap continues to evolve, with v4 set to be released in Q3 2024, promising greater customisability through the introduction of ‘hooks.’ A hook is a piece of code that can perform designated actions at key points throughout the lifecycle of a Uniswap liquidity pool (e.g. before or after a user swaps tokens in a given pool). Anyone will be able to build hooks.
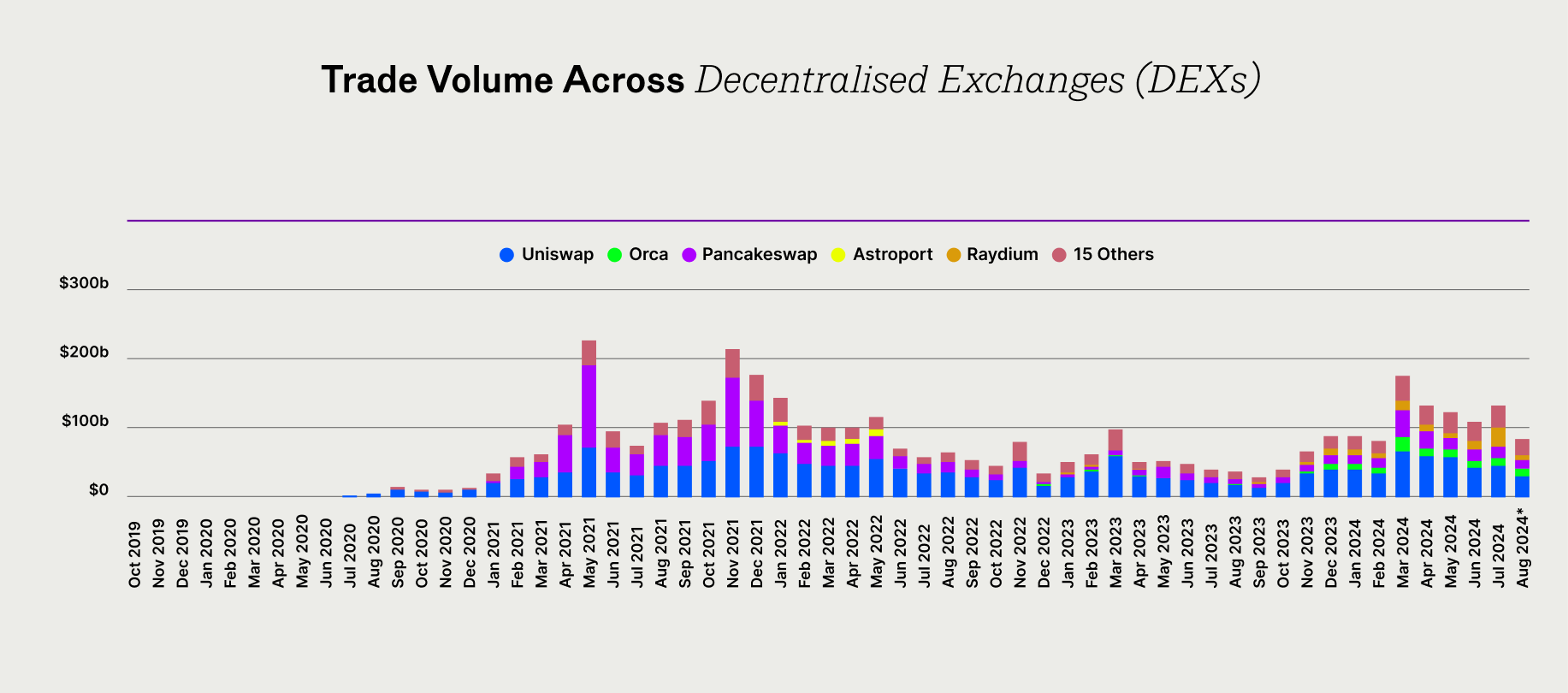
Source: The Block
Aave (AAVE)
Aave is a protocol that allows users to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies without the need for a centralised intermediary. Users can earn interest by lending their assets to liquidity pools or borrow against their crypto holdings, with interest rates determined algorithmically based on supply and demand. Aave is known for its innovative features, like flash loans and the ability to switch between fixed and variable interest rates.
Aave borrowing works on an over-collateralised basis, meaning that to borrow funds, you must deposit collateral greater than the amount you wish to borrow. This over-collateralisation allows Aave to automatically liquidate a borrower’s assets in the event of extreme price volatility, ensuring the safety of depositors’ funds.
The protocol has shown continued profitability, and combined with the proposal to implement a fee switch that would allow profits to be shared with token holders, there are strong fundamentals for continued upside in the AAVE token.
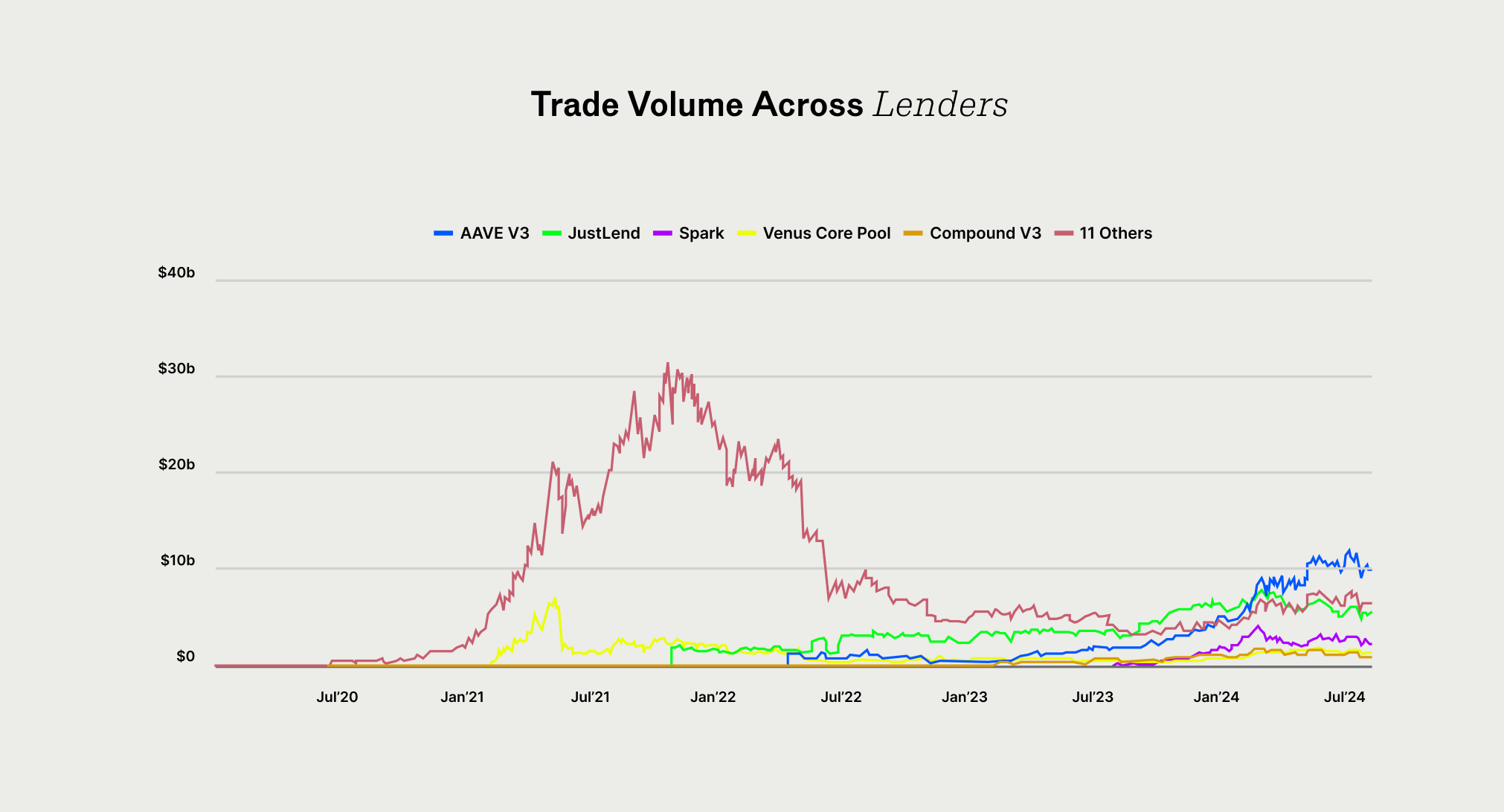
Source: The Block
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.
