Important
When withdrawing crypto from a wallet or an exchange, please ensure you do the following:
- Check that the public address is correct
- Choose a network to send on
- Check that the receiving wallet or exchange supports that network
- Test out the address by sending the smallest amount possible
- Once this has been received, send the remainder via the same network.
Sending cryptocurrency from one place to another can be very confusing for first-time users. One of the most common mistakes beginners make is selecting the wrong network to send their crypto across. This piece will discuss the most common blockchain networks and provide instructions for how to choose the correct one to ensure your transaction is successful.
The basics of blockchain networks
It is important to understand that there are different blockchain networks. Special care must be taken to ensure that you select the correct blockchain when sending your crypto. The receiving address must be compatible with the same network you are using to send the funds. It can be easy to choose the wrong network because addresses can be compatible with multiple networks.
Transferring crypto to another wallet or exchange that does not support the network you are withdrawing from will most likely result in the funds being lost. The process of recovering these funds is complex and difficult. In some cases, it isn’t possible to reverse a transaction over the wrong network and your crypto will be lost forever.
Learn how to deposit crypto from Binance to Swyftx.
Important To Remember
Choosing the wrong network when sending your crypto will result in funds not arriving at the receiving address. If you are unsure which network to choose it is always a smart idea to send a small test transaction the first time you are sending to a new receiving address to avoid mistakes.
The difference between networks
Crypto tokens are only compatible with the blockchain(s) they are built for transacting on. Each chain uses its own cryptography, which means each chain speaks its own “language”. Popular blockchains include: the Bitcoin Network (BTC), Ethereum Network (ETH), Binance Smart Chain (BSC), Polygon (Matic), and Fantom (FTM).
Many crypto assets were originally built on the Ethereum blockchain, however, many coins have evolved to become multiple-chain compatible through the process of “wrapped tokens”. For example, USDC is a stablecoin that does not use its own blockchain. It was built first on the Ethereum network as an ERC-20 token but is now compatible with other blockchains including Binance Smart Chain, Polygon (previously Matic network), Solana, Fantom, and others.
Did You Know?
Different blockchains can use the same address formatting starting with “0x”. This is one of the main reasons users mistakenly send crypto on the wrong network. Even though an address format might look identical, that does not always mean the sending and receiving networks are compatible.
Ethereum
Ethereum is one of the most popular early networks and was designed to enable other products to build on top of its infrastructure. Tokens compatible with Ethereum are called ERC-20 tokens. ETH is the native token for the Ethereum network. Each time a transaction takes place on the Ethereum network, ETH is used to pay the cost of the transaction.
Binance Smart Chain
The Binance Smart Chain (BSC) uses BEP-20 tokens that are built on the Binance blockchain. BNB is the network’s native token.
Polygon
Polygon (MATIC) is compatible with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and uses the same address format.
Fantom
Fantom (FTM) is a layer-1 blockchain that is fully compatible with Ethereum. FTM is the token that powers the Fantom network.
How do people send on the “wrong” network?
When sending crypto from an exchange to another address users are given the choice of multiple different blockchain networks. Often people will select the network with the lowest fees without checking if the wallet or exchange they are sending to is compatible with that network.
Key Takeaway
It is often attractive to simply pick the network with the cheapest fees or fastest processing times, but if these networks are not supported on the receiving side, then you risk losing your funds permanently.
Example of sending on the “wrong” network
Let’s say that Harold wants to send USDT from his Swyftx account to an external wallet. He puts in the amount he wants to transfer and the wallet address. He is given the choice of two different networks: ETH (ERC-20) or BSC (BEP-20). He chooses to make a transaction on the BEP-20 network because it is much cheaper. However, his external wallet doesn’t support the BEP-20 network so the funds will not arrive in his wallet as expected.
How to avoid sending crypto on the wrong network?
When withdrawing crypto you need to first check on the receiving end that the network is supported. The wallet you are depositing to must be compatible with the blockchain you are sending the funds from.
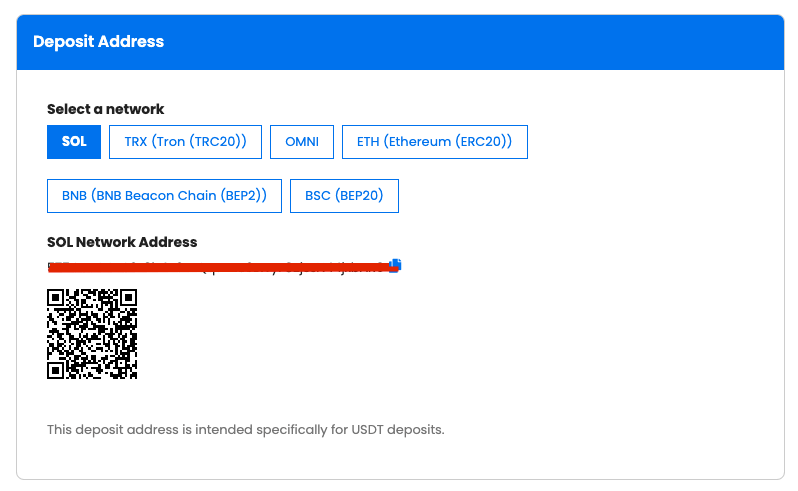
The screenshot below displays the Tether USD (USDT) deposit page on Swyftx. Under the “Select a Network” text, there are six supported networks. When depositing into this particular Swyftx wallet from another wallet or exchange, the user must select one of these networks.
A common mistake users make when depositing USDT into Swyftx is choosing the Polygon network. This network is not supported by Swyftx and therefore USDT deposits via Polygon will not arrive in their account.
If you are ever in doubt about a transaction, you can follow this checklist to make sure you are sending on the correct network:
- Check that the public address is correct
- Choose a network to send on
- Check that the receiving wallet or exchange supports that network
- Test out the address by sending the smallest amount possible
- Once this has been received, send the remainder via the same network.
Memo codes or Destination Tags
Transaction on some networks, such as Stellar (XLM), Cosmos (ATOM), and Ripple (XRP), will require additional information in the “Memo” field. In a similar way to when you pay your rent for example, the bank will require an extra “reference code” before sending funds, so the receiver is able to identify who the transaction is from. A message like the below will tell you if this is needed for your transaction. Always make sure to check on the receiving end if a Memo code is provided in order to receive the transaction. If you fail to do this you will lose your funds.
Important To Remember
You MUST include both the address AND the MEMO (or Destination Tag) for incoming deposits. Failure to do so may result in the permanent loss of funds. Please contact us before sending if you are unsure.
Recovering crypto transferred on the wrong network
Recovering crypto sent on the wrong network can be a complicated process and is best to be avoided, as in some cases it is not possible. However, you may be able to import your private key or seed phrase into a new wallet that supports both networks. In this case, you should be able to access your lost funds.
MetaMask is an example of a wallet that is compatible with multiple networks. Please note this method is available only for users of non-custodial crypto wallets. This method will not work when sending to an exchange.
Wrap up
The receiving wallet or trading platform will determine which networks are supported for incoming transactions. Many networks are based on the same protocols, so addresses can be identical. It is imperative that you check on the receiving end that the address accepts transactions across the same network you are sending from.
This guide has provided a clear explanation of some of the different blockchains and described the importance of selecting the correct network to ensure that your crypto is sent successfully. If you would like to learn more about blockchain technology, crypto wallets, or anything else crypto-related, there is plenty of great content available on Swyftx Learn.
Quiz
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.

 Article read
Article read