A gas fee, also referred to as a transaction fee, is a term that describes the pricing mechanism on the Ethereum blockchain. This is a fee charged for executing transactions and smart contracts. These fees are paid in Ether (ETH), the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network. This article will discuss why Ethereum charges gas fees, how to calculate them, and how Ethereum 2.0 will lower gas fees.
Why does Ethereum charge transactions fees?
Cryptocurrencies and other DeFi applications use blockchain technology to operate. A blockchain is a public ledger that records and displays all the transactions that are processed on a given network. Blockchain technology functions by having multiple computers or ‘nodes’ that work to verify these transactions. This is how it is able to operate without one central entity controlling the network like they do in traditional banking and finance systems.
On a network like Ethereum, transactions are verified by miners (also referred to as validators). In addition to protecting the network from attacks, these miners also streamline transactions so that the Ethereum blockchain does not get overloaded. Gas fees are required to compensate for the computing energy needed to process and validate transactions. Miners are incentivised to validate transactions before other miners in order to earn ETH from the gas fees.
Key Takeaway
Ethereum charges gas fees in order to compensate miners for the computational power and energy they spend verifying transactions and executing smart contracts.
Which transactions require gas?
The Ethereum platform isn’t just limited to cryptocurrency transactions. Its network has the capability to execute smart contracts, run decentralized applications (dApps), and create or transfer ERC-20 tokens. Gas is the unit for measuring the amount of computational effort used to perform each task. However gas does not have a monetary value. Each type of transaction requires a different amount of gas units to run. For example:
- Adding two numbers = 3 gas units
- Getting the balance for an account = 400 gas units
- Sending a transaction = 21,000 gas units.
Peer-to-peer transactions on Ethereum are also subject to gas costs. Typically, the wallet or exchange that is used to send the ETH will have an estimate of how much gas is required to complete the transaction. Demanding transactions that require validation will naturally incur higher gas prices.
Smart contracts used for dApps will usually have a combination of nodes working together. Therefore a combination of gas units is required to allow the program to run. Some time-sensitive smart contracts can take hundreds of thousands of gas units.
How to calculate gas fees
It is important to understand how much gas is required to complete a transaction. Failure to pay gas fees will result in an incomplete transaction. The amount of gas you need also depends on how large your contract or transfer is and how fast you want it to be executed. Gas units are denoted in GWEI which is a billionth of an ETH (or 0.000000001 ETH). GWEI is used to mitigate the risk of ETH price fluctuations affecting gas costs.
Each transaction on Ethereum also has a gas limit. This determines the maximum amount someone is willing to spend on a transaction. A higher gas limit means that more effort is required to execute that particular transaction or smart contract. Having a gas fee and a gas limit incentivises the developers to keep their smart contracts as simple and precise as possible. This works well as it reduces network congestion.
Why are gas fees so high?
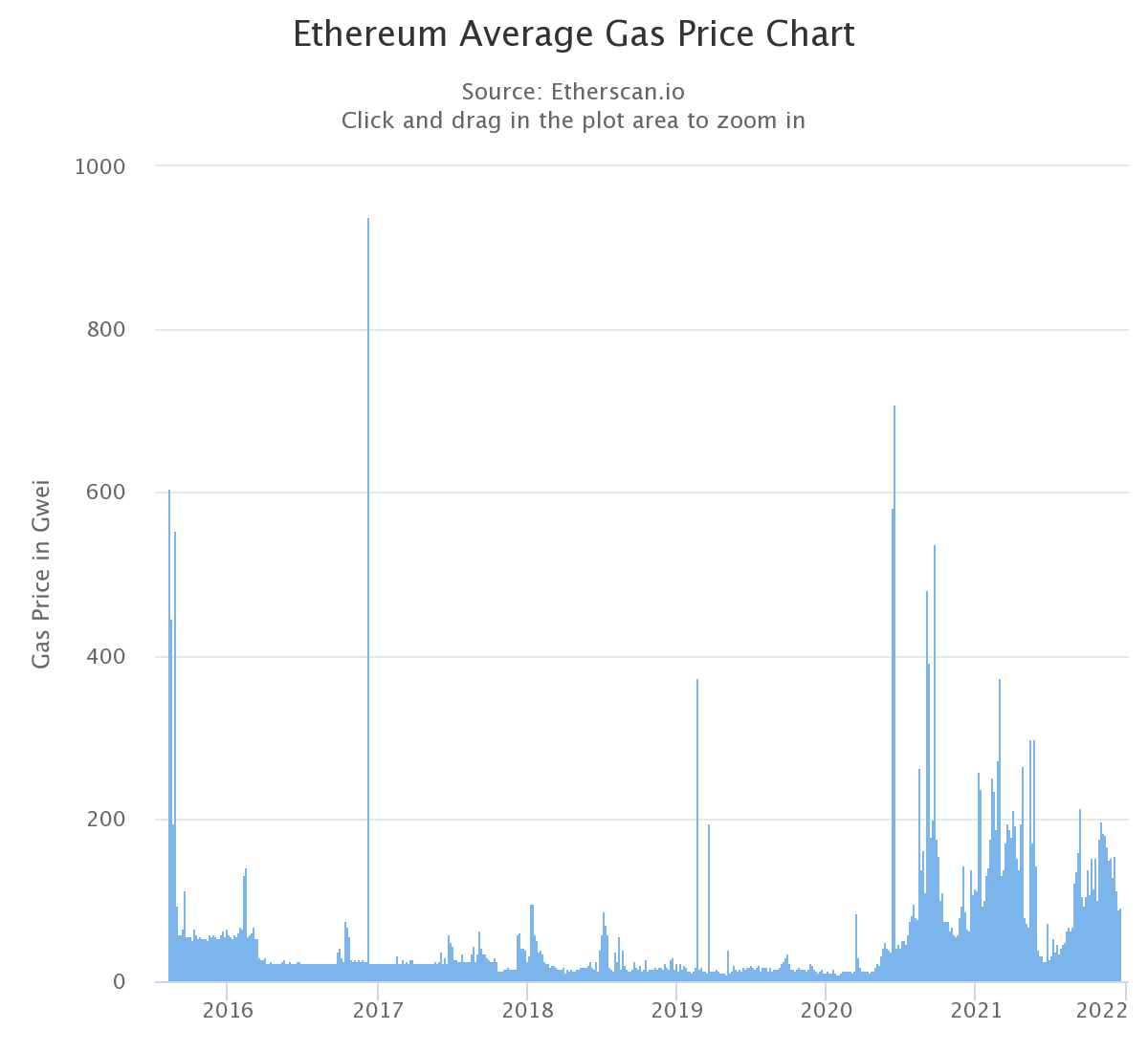
In May 2021, gas fees hit an all-time high of $4300 USD, following a price surge in Ethereum. Gas price typically increases when the popularity of Ethereum rises. When there are more people transacting through the Ethereum network, miners have more options to choose from and can prioritise higher transaction fee projects. If a transaction or project is urgent and needs validation quickly, then it’s likely that the gas fee will be high.
How to reduce gas fees
If a project isn’t time-sensitive then it may be best to wait for the gas prices to lower. Gasnow.org and etherscan.io are two reputable websites that track and report Ethereum gas prices. One simple way to reduce the gas price is to time your transaction well. Gas fees tend to fluctuate throughout the day. Check out the gas fee fluctuations for the past week to see when the cheapest gas fees occur.
How will Ethereum 2.0 lower gas fees?
There is a lot of excitement about the upcoming Ethereum 2.0 update. Ethereum 2.0 aims to improve the scalability and security issues of the blockchain. The main component of the upgrade is to move from its current Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to the more efficient Proof of Stake (PoS). This will allow miners and validators to use their ETH as leverage to keep the platform running and secure. The new PoS system will reduce the energy consumption of Ethereum by roughly 99.5%.
The current infrastructure of Ethereum is able to process a maximum of 15 transactions per second, while Ethereum 2.0 will be able to process thousands of transactions per second. Vitalik Buterin and the entire Ethereum team are optimistic that gas prices will decrease with the launch of Ethereum 2.0. Given the number of transactions per second will significantly increase, this will reduce congestion on the platform which in turn will reduce gas fees.
How to invest in Ethereum 2.0
Although Ethereum has not yet officially transitioned to Ethereum 2.0, you can buy ETH on the Swyftx crypto exchange. This will automatically convert to ETH 2.0 once the upgrade on the network is complete. The price of ETH 2.0 will be identical to the price of ETH.
Summary
Gas fees are charged for executing transactions and smart contracts on the Ethereum network. Gas fees are an essential part of the operation of the blockchain, however, during times of congestion the prices can skyrocket. The Ethereum 2.0 upgrade aims to solve this, but until then patience and making transactions at strategic times are key to reducing gas fees. If you’d like to learn more about Ethereum, smart contracts, or blockchain technology, there is lots of great content on Swyftx Learn!
Next lesson
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.

 Article read
Article read