An Automated Market Maker (AMM) is a critical element of the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. Like any other market, the DeFi market requires liquidity in order for market participants to easily trade assets. Unlike traditional markets, however, the DeFi ecosystem doesn’t rely on market participants to provide liquidity.
Automated market makers ensure the DeFi ecosystem remains liquid at all times through liquidity pools. In simple terms, AMMs are automated robots that ensure a market participant is always able to trade an asset.
What is an Automated Market Maker?
AMMs are financial tools unique to the DeFi ecosystem. The core purpose of automated market makers is to address the problem of liquidity on a decentralized exchange (DEX).
Decentralized exchanges are a relatively new innovation within the cryptocurrency ecosystem and, in many cases, are technically complex. This reduces the total number of buyers and sellers on DEXs which, in turn, limits market liquidity.
AMMs solve this problem by creating pools of liquidity that can be contributed to by anyone. Users of platforms that integrate automated market platforms trade against a liquidity pool. In simple terms, a liquidity pool is a shared pool of an asset — such as a blockchain token — with the price of the asset determined by a mathematical formula.
The assets held within a liquidity pool are traded via an algorithm, rather than the limit order book model used in traditional markets.
Key Takeaway
Automated market makers (AMMs) allow users on a decentralized exchange to automatically trade without permission using liquidity pools.
Traditional market makers vs. Automated market makers
Traditional financial markets rely on buyers and sellers to create liquidity. On traditional exchange platforms, buyers and sellers list assets at varying prices. When one party finds the price set by another party acceptable, a trade is executed, determining the price of the asset.
Most traditional markets, such as securities, precious metals, international currency markets operate in this manner. Within the context of traditional markets, a market maker is a company or individual that is able to execute both buy and sell orders at market price on a continuous basis.
Professional market makers in traditional industries, however, are tightly regulated and highly centralized — it’s not possible for anybody to get involved with traditional market-making. The DeFi ecosystem, however, is decentralized, is open 24/7, and allows anybody to become a market maker by participating in liquidity pools.
How does an AMM work?
AMMs have become the standard system through which digital assets are traded within the DeFi ecosystem. They function in a similar manner to traditional order book exchanges at first glance.
Like traditional exchanges, AMMs offer trading pairs, such as ETH/USDT. Unlike traditional exchanges, however, AMMs don’t pair market participants with a counterparty to trade with through an order book.
Instead, trading pairs exist as liquidity pools, such as an ETH/USDT liquidity pool. Market participants interact with a smart contract that creates the market for them, rather than with a counterparty.
The ratio of assets within an AMM
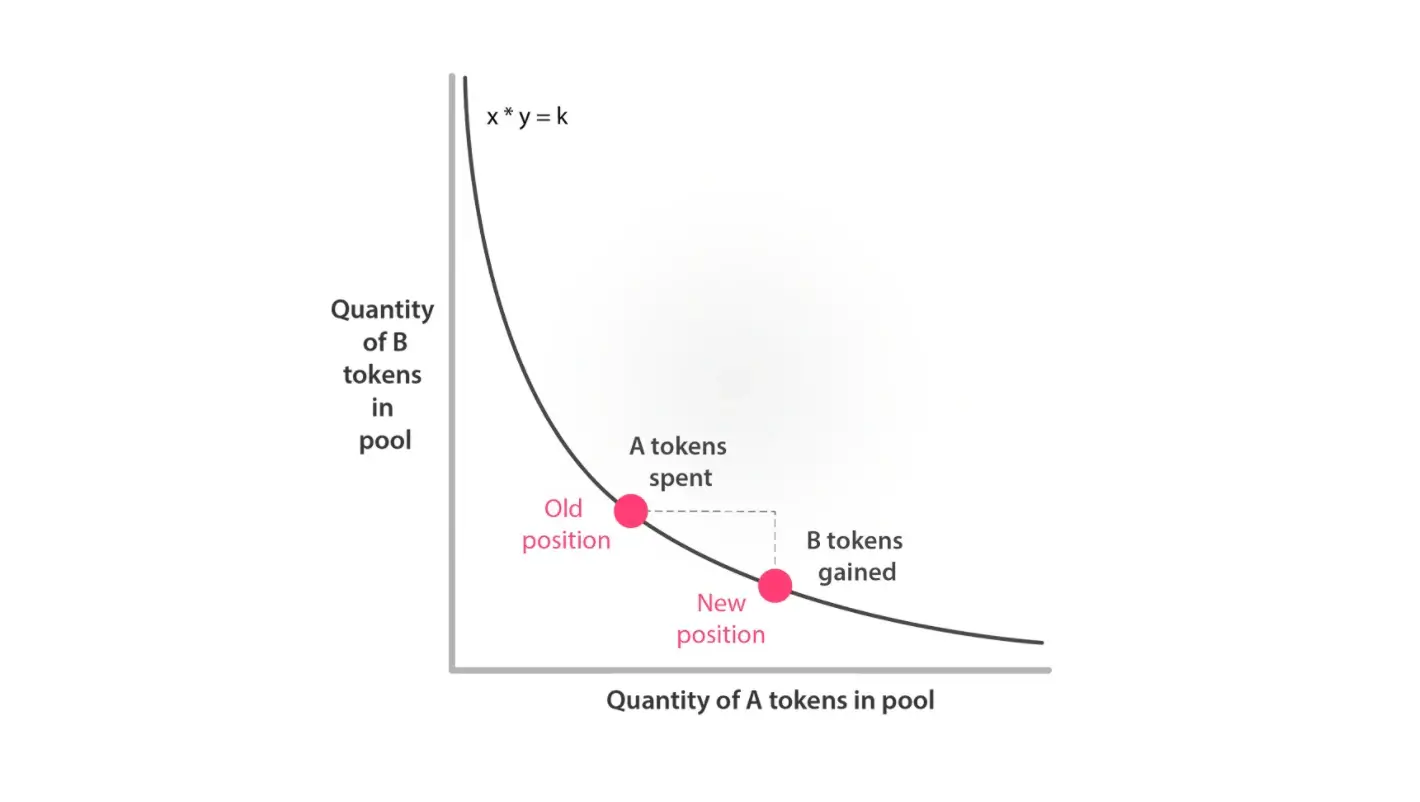
In order to balance the ratio of assets within a liquidity pool, automated market makers use a mathematical formula. This formula, simplified by Uniswap, is present as follows:
x * y = k
Within this formula, the constant is represented by k, and ensures that there is a balance of assets that determines the price of the assets within the pool. The trading pairs within the pool are represented by x and y (i.e. ETH and USDT)
If, for example, an AMM has two volatile assets within the liquidity pool, the purchase of one ETH would result in an increase in the price of ETH and remove one ETH from the pool. The price of USDT, therefore, decreases and adds another USDT to the pool.
This formula ensures that the pool remains in constant balance. When expressed on a graph, the prices of assets within an automated market pool follow a curve. Purchasing one x from the pool pushes the price of x above the curve, while the sale of x pulls the price of x below the curve.
Should the value of an asset within an AMM pool vary significantly from market prices within the broader market, traders will leverage arbitrage opportunities between the broader market and the automated market maker to balance it.
What Are the Risks of Using an Automated Market Maker?
The most common risk presented by the use of AMMs is the potential of impermanent loss when providing liquidity to a pool. Impermanent loss refers to the temporary loss of funds when there is volatility in the trading pair within a liquidity pool. It is the risk users take when providing liquidity to liquidity pools in exchange for fees the earn as rewards.
AMMS don’t automatically adjust prices. If the value of an asset in a liquidity pool splits apart from the price curve of the automated market makers, arbitrageurs will extract value from the liquidity pool and therefore from a liquidity provider. Thus resulting in impermanent loss.
Automated Market Maker Examples
The DeFi ecosystem is currently dominated by three different AMMs models — Uniswap, Balancer, and Curve:
- Uniswap allows anybody to create a liquidity pool of ERC-20 tokens with a 50/50 ratio and is currently the most widely-used automated market model on Ethereum.
- Balancer is similar to Uniswap, but allows users to create dynamic pools that can consist of up to eight different assets in different ratios.
- Curve focuses on solving the liquidity problem by crating liquidity pools of similar assets, such as stablecoins, and is notable for offering highly efficient trades.
Did You Know?
The majority of decentralized exchanges (DEXs) such as Uniswap, Curve, Balancer, Raydium and Bancor use AMMs.
Summary
AMMs serve two important functions within the DeFi ecosystem. For liquidity providers, automated market makers present an opportunity to generate profit by committing assets to a liquidity pool.
For traders, automated market makers make it possible to instantly trade one asset for another in a decentralized trading environment.
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.
