How has the Bitcoin halving affected the price of Bitcoin?
The Bitcoin halving event has regularly been followed by BTC reaching a new all-time high price within 18 months of the event.
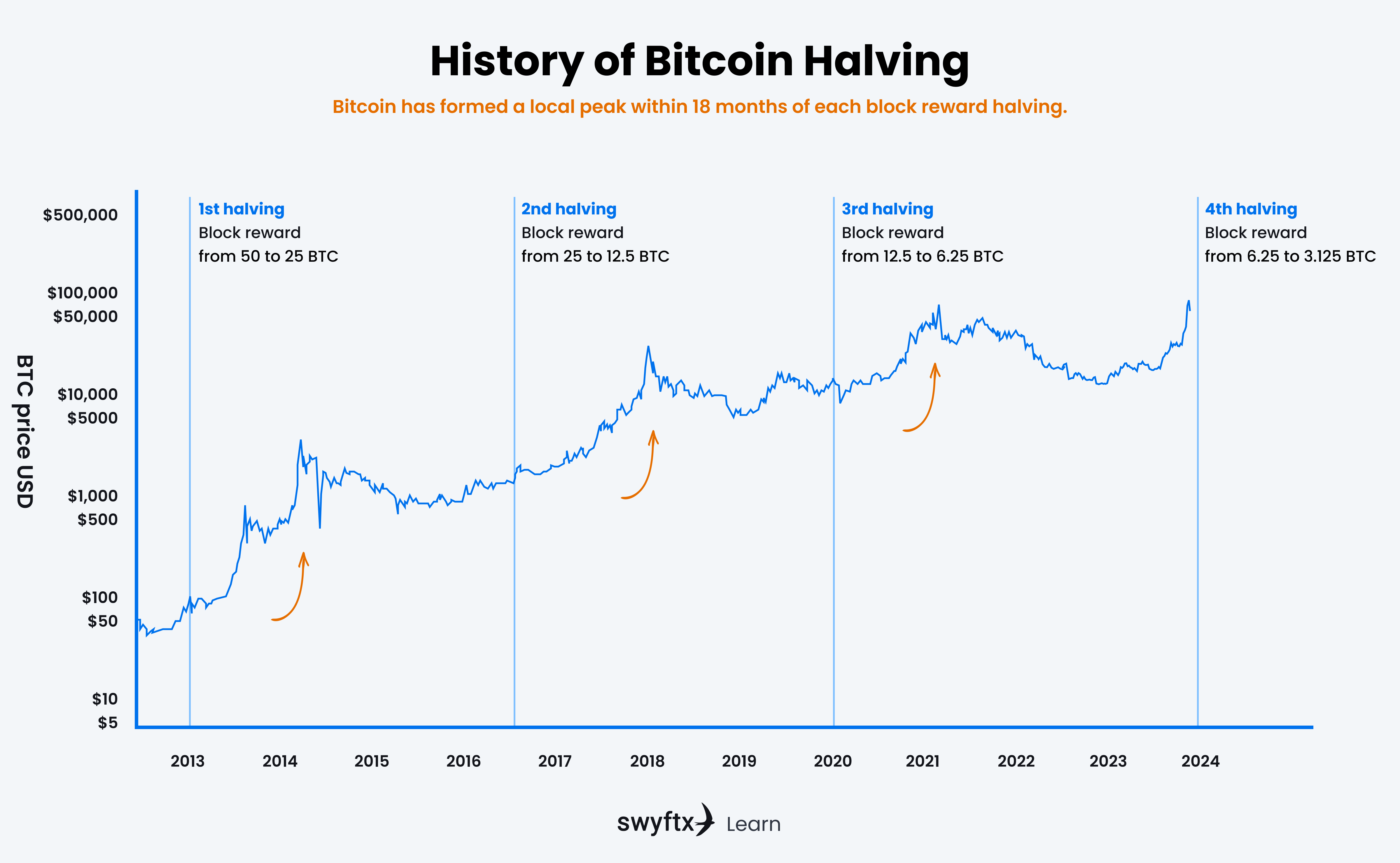
Historically, it can take over a year for the halving’s impact on supply to fully set in. For example, Bitcoin’s very first halving occurred in 2012 when the price of one BTC was approximately $12 USD. By early 2014, Bitcoin was trading at $1,214. 2016’s halving demonstrated a very similar theme, with BTC ballooning from $647 to nearly $20,000 over the following 18 months.
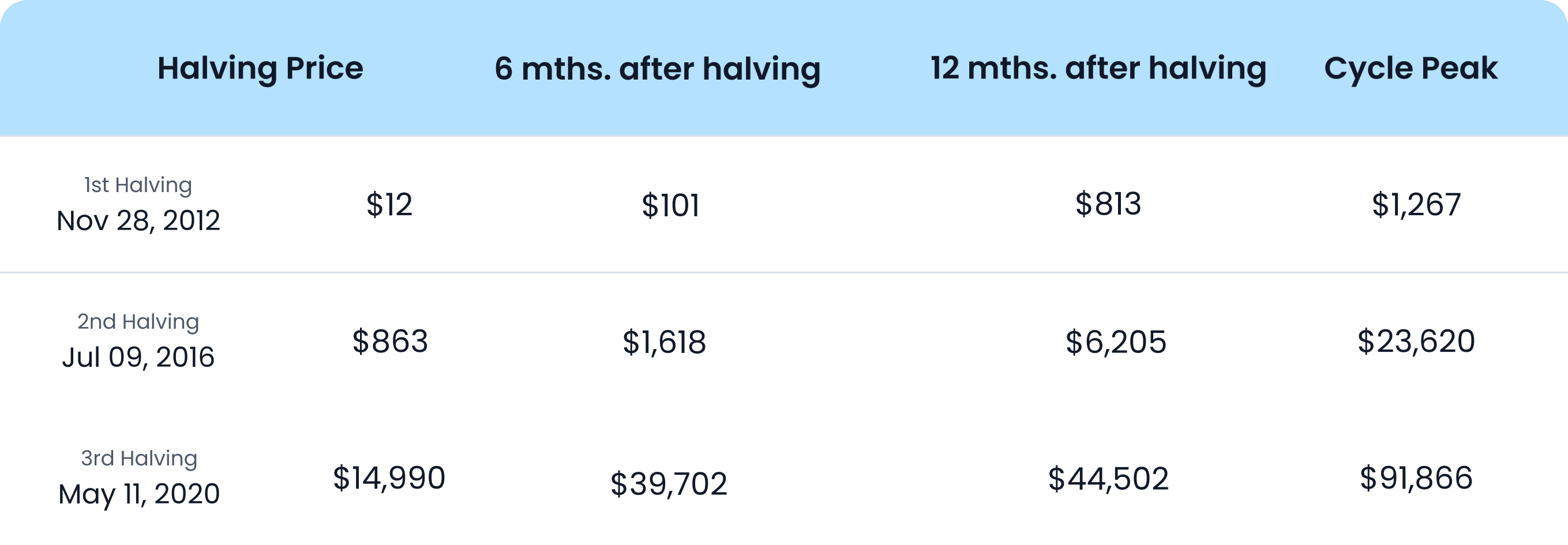
All values are in AUD, approximate figures and sourced from TradingView in USD and then converted to AUD using the exchange rate at the time.
Why does the Bitcoin halving historically increase BTC’s price?
Bitcoin’s price historically rises after halvings due to supply and demand fundamentals. The amount of BTC rewarded to miners reduces the amount of Bitcoin entering circulation. If more investors wish to purchase BTC following a halving, it becomes harder due to the increased scarcity of new supply. If demand outpaces supply, upward pressure is placed on BTC’s price causing the historic bullish swings we associate with halvings.
Will Bitcoin’s price rise after the next halving?
Investing in Bitcoin leading into a halving can seem like a home run. However, Bitcoin does not exist in a vacuum, and its price is ultimately determined by the market. If there are more sellers than buyers, diminishing supply doesn’t matter – Bitcoin’s price will not increase.
Several factors make the upcoming 2024 halving a little different from previous scenarios. The global world is still recovering from the supply shock caused by the COVID-19 lockdowns, with both inflation and interest rates relatively high. These macroeconomic factors tend to dissuade more volatile investments like BTC, as investors look toward cash or defensive assets. A halving event has never occurred amid such high global interest rates.
On the flipside, the approval of Bitcoin ETFs in the United States has meant big financial institutions like BlackRock and Fidelity are buying up much of the available BTC. These ETFs have been extremely popular since launching in January 2024, attracting hundreds of millions of dollars in investments into Bitcoin everyday on average since inception and have made Bitcoin one of the most popular assets on Wall Street and amongst institutional investors this year.
This surge in demand, coupled with the decreasing supply from the block reward halving, could lead to a significant increase in Bitcoin’s value.
Wrap up
When a Bitcoin block is successfully committed to the Bitcoin blockchain, the miner responsible receives block rewards in the form of freshly minted Bitcoin. Halving is a key function of the Bitcoin blockchain that separates it from inflationary currencies, because of its locked total supply mechanism and, as a secondary effect, increases scarcity of new supply, which has the potential to drive Bitcoin price increases in the right market conditions.
This article has discussed the basics of the Bitcoin blockchain and explained what Bitcoin halving is and how it affects the price of Bitcoin. If you would like to learn more about Bitcoin mining, blockchain, and other topics there are plenty of great resources on Swyftx Learn!
Quiz
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.


 Article read
Article read

