Inflation is one of the most pivotal factors when assessing an economy’s health. Too little inflation often indicates a stalling GDP, while runaway inflation can cause a cost-of-living crisis and tough fiscal policies. The gravity of inflation, and its related metrics, can have a major impact on the financial markets — including crypto. That’s why understanding inflation basics can help provide insight into why the markets might be trending up or down on any given day.
What is inflation?
At its simplest, inflation is the rise in the cost of goods and services households buy. This might look like the price of petrol rising, your weekly grocery shop going up, or renting an apartment becoming more expensive.
As the cost of living inflates over time, the purchasing power of a dollar steadily decreases. In simple terms, a dollar today will get you less than a dollar in ten years — thanks to inflation.
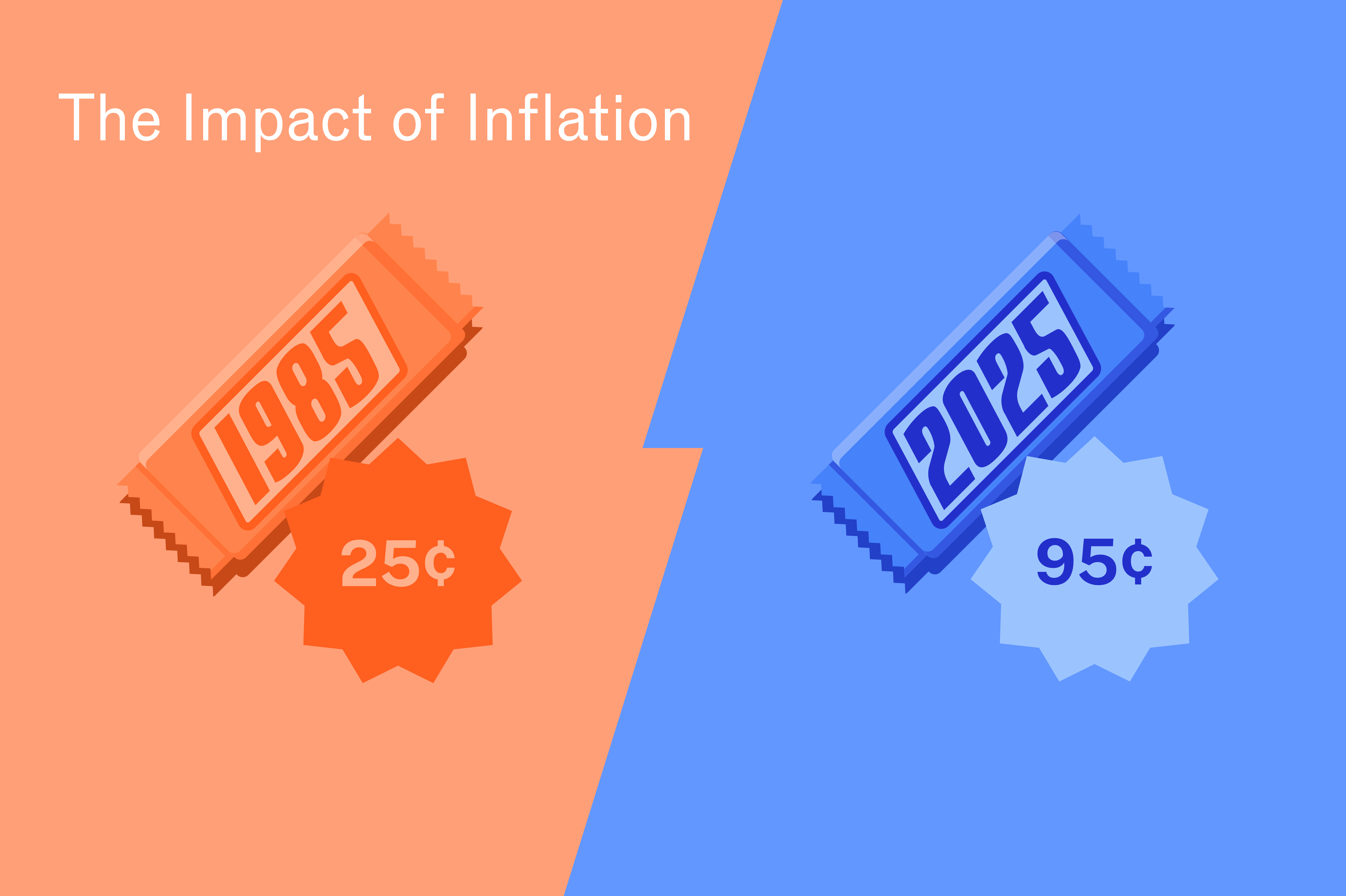
Did You Know?
Although inflation is a loaded term, most Governments strive for a small amount of inflation every year — typically around 2%. This is because inflation can demonstrate a healthy level of growth for an economy, with more money floating around for businesses and consumers.
Types of inflation
The Reserve Bank of Australia recognises three primary causes of inflation in Australia: cost-push inflation, demand-pull inflation and inflation expectations.
Demand-pull inflation
Demand-pull inflation occurs where the demand for goods and services outpaces their total supply. This can arise due to increased consumer, business and government spending. With greater overall demand, producers can mark up prices — leading to inflation.
Meanwhile, with overall output growing and unemployment low, businesses often need to pay employees more to attract them. As wages grow, so too does spending power, which can lead to the demand-pull inflation cycle running out of control without intervention.
Key Takeaway
Imagine a fast-growing city where alluring job opportunities attract more and more people. Meanwhile, the supply of housing in the region remains the same. With the population surging, buyers and renters compete with one another to secure residency in the region — causing demand to outpace supply. This is an example of how demand-pull inflation might take shape in an individual market.
Cost-push inflation
Cost-push inflation is caused by the total supply of goods and services within an economy falling. Essentially, the potential output of an industry (or several) drops while demand remains the same. This is often caused by the rise in price of production, whether that’s the cost of labour or raw materials like iron ore.
Short-term weather events are an example of cost-push inflation. For example, a cyclone in Brisbane might cause a supply disruption for bananas, resulting in their price ballooning across Australia. This can have a flow-on effect when buying things from dessert restaurants, bakeries and so on.
Inflation expectations
Like a self-fulfilling prophecy, the mere expectation of prices rising in the future can cause it to become reality. Simply put, a business, expecting the rate of inflation to accelerate in the coming months, might pre-emptively increase the costs of their goods and services to consumers. Everyday households may also adjust their spending patterns or demand better wages depending on expectations.
Measuring inflation
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
Each nation tends to have its own cornerstone indicator when measuring inflation. Down under, the Reserve Bank of Australia relies upon the Consumer Price Index (CPI). This metric tracks the price of certain goods and services over every three months.
Because inflation is unique for different goods and services, the CPI must boil this down to one overall figure reflecting the broader economy. So, the more the average pay cheque goes toward a product, the heavier its weighting when measuring CPI.
The RBA includes a wide range of products in its calculations, including the cost of basketball shoes, heart surgery, attending the footy or buying your favourite beer.

Important to Remember
In the United States, the Federal Reserve Bank reports on several inflation metrics. CPI is the most well-known, but their preferred measurement is actually the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Index. The PCE excludes volatile items like fuel, energy and fruit and includes spending made on behalf of consumers. This might include Government healthcare costs or education scholarships.
Interest rates
Interest rates are levers a government can pull to increase or decrease the cash flow in an economy. These policies can be used to rein inflation back toward the target rate. In Australia, the cash rate is determined by the Reserve Bank of Australia.
Many believe that interest rates directly relate to mortgage payments — that is, how much people need to repay banks for loans on their property. In reality, it’s the interest rate on unsecured overnight loans between banks.
When this rate changes, it impacts how expensive it is for Australian financial institutions to borrow from one another. This is then passed onto consumers and businesses, through products like mortgages, Government bonds and high-interest savings accounts.
Because of this, a nation’s cash rate can provide insight to the broader economy. For example, if the RBA drops rates significantly in a short period of time, it can indicate stalling growth. By lowering the interest rate, the Reserve Bank is trying to stimulate economic activity like spending, borrowing and investing.
How does inflation impact the crypto market?
Inflation can have a huge impact on the crypto market in several ways.
A high-inflation environment means that the spending power of fiat currency is dropping. So, instead of holding money in cash, investors might attempt to ‘hedge’ against debasement by purchasing alternative assets like cryptocurrencies.
More commonly, inflationary environments can negatively affect crypto prices. When a government tightens fiscal policies by raising interest rates to combat inflation, it makes borrowing money more expensive for institutions and consumers.
With less cash flow in the economy, investors can be inclined to move away from risky, volatile assets (like equities and cryptocurrencies). Instead, lower-risk yields like Government bonds and high-interest saving accounts can become more attractive. This is amplified by higher cash rates improving on-paper returns for such products.
The importance of United States fiscal policy
As one of the world’s largest economies, inflation in the United States can significantly influence crypto market performance. As an Australian, there may have been times you’ve woken to a sea of red in the market and wondered to yourself, “What is going on?”
Historically, monetary policy in the United States has a notable impact on the prices of cryptocurrencies.
In June 2022, at the height of inflation, the US Feds hiked the cash rate by 0.75%, which played a major role in Bitcoin’s price tumbling 10% over the next 24 hours.
Keeping an eye on these metrics work can help traders make short-term investment decisions and better understand market trends.
For example, if the Federal Reserve identifies CPI running higher than anticipated, investors might sell more volatile assets, expecting the national cash rate to rise.
However, if PCE data comes out a week later and demonstrates US inflation is moving as forecast, investors might pivot back to crypto, as the potential of an interest rate cut becomes more likely.
The chart below demonstrates that, while monetary decisions in the US can influence Bitcoin’s price – especially in the short-term – it is just one of many factors that must be considered.

Summary
Inflation has a huge impact on the economy. It’s (one of) the reasons why a Quarter Pounder from McDonald’s is double the price it was earlier in the decade. As governments act to combat too much — or too little — inflation, it can lead to complex monetary policies that make borrowing funds more or less expensive. This has an inherent impact on all financial markets, including cryptocurrency.
By following key inflation metrics, investors can avoid being blindsided by big fiscal changes, better understand global economic trends and prepare accordingly.
Next lesson
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.


 Article read
Article read