Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) are blockchain-based organizations that are designed to operate autonomously in accordance with rules enforced via code typically through smart contracts. By relying solely on code to enforce rules, DAOs theoretically eliminate the need for human intervention and therefore eliminate human error.
This piece will explain what DAOs are and how they work. It will cover how DAOs utilise governance tokens. And it will look at some of the most popular examples and discuss the pros and cons of using a DAO.
What is a DAO?
A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) is an organizational model that utilizes blockchain technology to overcome the most significant obstacle present within any organization: the principal-agent dilemma.
The principal-agent dilemma
The principal-agent dilemma refers to the relationship between the two types of stakeholders in virtually every organization. An “agent” is an individual or entity that is permitted to execute actions or make decisions on behalf of another. The “principal” is the individual or entity who is represented by the agent. For example, a soccer manager (agent) makes decisions about which players (principals) are in the squad and what positions they will each play.
There are many factors that create friction between an agent and a principal within traditional organizations. A decision-maker may operate with different goals or priorities than the party they make decisions for. To use the previous example, the soccer manager may want to play his most promising player in a forward role, however, she might feel that she’s better in a defender role. A lack of transparency or inefficient information access between parties can impede the efficiency of an organization.
How DAOs solve the principal-agent dilemma
A traditional organization can take a broad spectrum of forms, ranging from private entities such as corporate governance models to public entities such as state governments. Most of these are forms of centralized leadership. The DAO model aims to eliminate the need for human intervention in organizational governance, solving the problems presented by traditional organizational models.
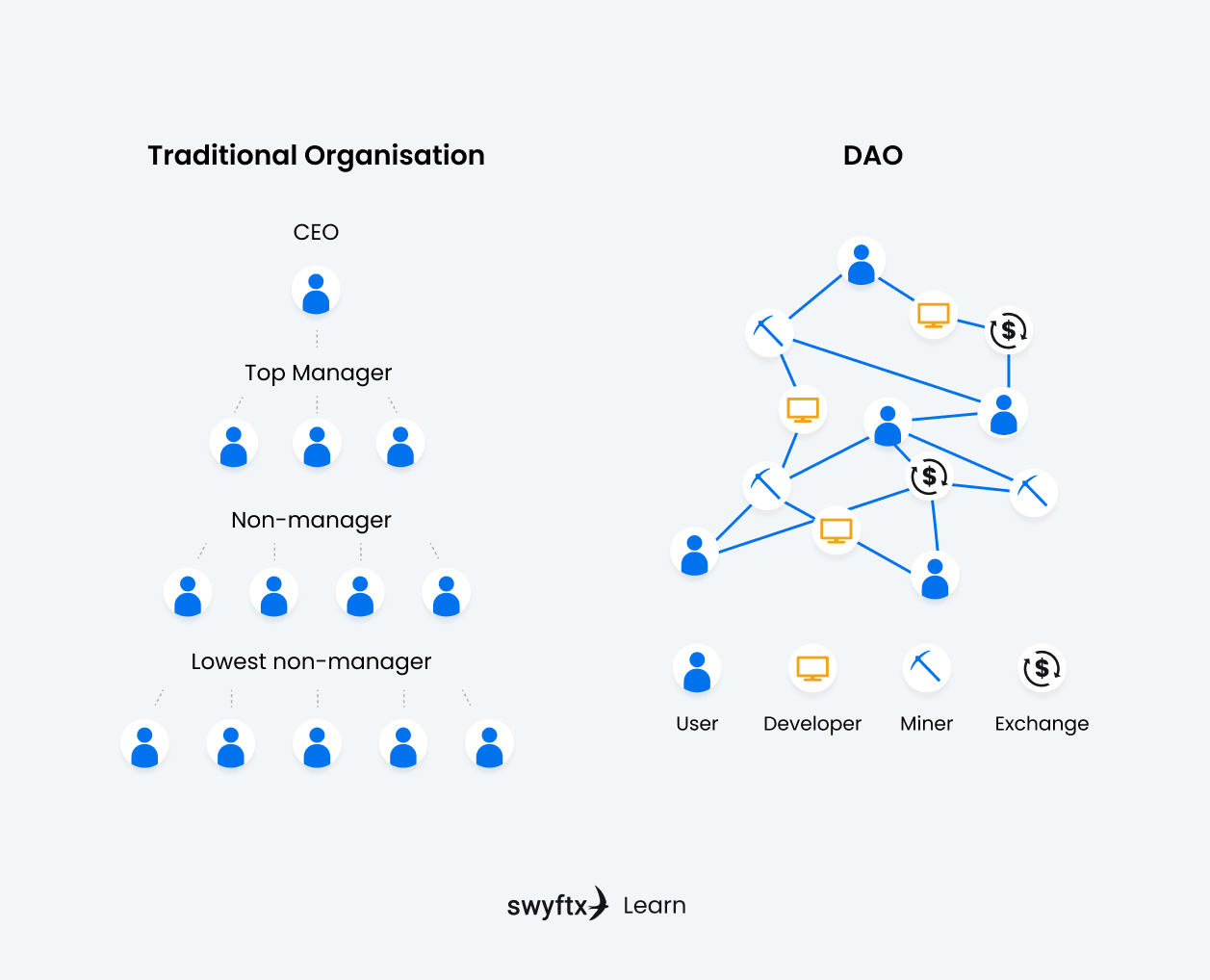
Figure 1 – Traditional organization vs a DAO
A DAO uses smart contracts and computer code to enforce the structure and flow of information within an organization, ensuring that the incentives of all stakeholders are aligned. Put simply, a decentralized autonomous organization creates an immutable, code-enforced organization that cannot be tampered with by stakeholders or interfered with by centralized third parties.
Key Takeaway
DAOs operate in accordance with instructions laid out in smart contracts that are executed automatically when specific conditions are met. This allows DAOs to facilitate decentralized decision-making, high levels of efficiency, and extreme transparency, creating “trustless” systems.
How Does a DAO Work?
There are many different DAO models that operate with a broad spectrum of different mechanisms. All DAOs, however, are established in a similar manner.
The first step taken when establishing a DAO involves defining the rules of the organization and encoding them into a smart contract that can be executed on the blockchain. This process typically takes into account the operation of the DAO, incentive structures, and the governance system of the organization, as well as the way in which changes will be made to the DAO in the future.
Once the DAO’s rules are defined, the DAO will require funding. A corporation founded via a DAO may issue equity via a token that can be used within the DAO in corporate governance mechanisms or to incentivise specific activities. Individuals or entities interested in participation in a DAO are able to purchase these crypto tokens in return for capital, which is used to fund the DAO.
Finally, the DAO is deployed. Individuals or entities that hold DAO tokens become stakeholders and are able to participate in the governance process. A DAO tokenises the value a stakeholder possesses within an organization and ensures that all value transfers within the DAO are executed in a transparent and fair manner.
Key Takeaway
Token holders are given voting rights to participate in the governance (or voting system) of the DAO.
What are the advantages of DAOs?
The structure of a DAO ensures that the organization is able to operate independently of human interaction. A DAO does not need arbitration from its creators, parties, or central authority.
The open-source nature of DAOs means that the rules they operate in accordance with, and all activities performed within and by the DAO, are recorded on an immutable public blockchain. This ensures that all participants within a DAO operate with a common goal, making decisions through a democratic blockchain-based voting model.
What are the disadvantages of DAOs?
The most significant disadvantage presented by the DAO model is the risk of human error. Particularly in the development of this complex, autonomous decision-making framework. One which is responsible for the management of large amounts of money.
The presence of exploits within an improperly coded DAO represents a major problem that must be overcome by DAO developers.
Did You Know?
The first DAO, launched in 2016 on the Ethereum network, was intended to operate as a decentralized venture capital firm directed by the Ethereum community. Three months after launch, the DAO was hacked and DAO members lost $60 million USD worth of ETH, demonstrating the importance of robust, secure code in DAO composition.
Notable DAO Examples
While the first example of an operational DAO, the Ethereum DAO, resulted in failure, there are now multiple successful blockchain projects that function as strong examples of successful DAOs.
MakerDAO
MakerDAO is a decentralized finance (DeFi) project built on the Ethereum blockchain that facilitates decentralized lending. MakerDAO is directed by the MakerDAO foundation, which operates with a number of structural elements that draw from the DAO model. The MakerDAO foundation now operates in a completely decentralized manner, with holders of the MakerDAO governance token (MKR) participating in decentralized decision-making.
Uniswap
Uniswap is one of the most popular exchanges in the sphere of DeFi. The Uniswap platform issued their UNI governance token in September 2020 with the goal of establishing Uniswap as a community-owned protocol.
DASH
Payments-focused cryptocurrency, DASH, operates a decentralized decision-making process through a governance token issued to master nodes.
Wrap up
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) leverage the transparent and unchangeable, code-enforced nature of blockchain to create independent governance and organizational systems that are immune to human error or interference.
While the methodology and technology that drives the development of DAOs is still in the early stages, the DAO model holds the potential to establish self-governing, transparent organizations in virtually any industry, application, or use case.
Disclaimer: The information on Swyftx Learn is for general educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any assets. It has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and does not purport to cover any legal or regulatory requirements. Customers are encouraged to do their own independent research and seek professional advice. Swyftx makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content. Any references to past performance are not, and should not be taken as a reliable indicator of future results. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose. Consider our Terms of Use and Risk Disclosure Statement for more details.
